Online courses directory (391)
By Luca Trevisan
This topic will add a ton of tools to your algebraic toolbox. You'll be able to multiply any expression and learn to factor a bunch a well. This will allow you to solve a broad array of problems in algebra. Factoring Special Products. Example 1: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 1. Example 2: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 2. Factoring to produce difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 3. Example: Factoring perfect square trinomials. Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression. Example: Factoring special products. Multiplying Monomials. Dividing Monomials. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 1. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 2. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 3. Monomial Greatest Common Factor. Multiplying binomials word problem. FOIL for multiplying binomials. Multiplying Binomials with Radicals. Multiplying binomials example 1. FOIL method for multiplying binomials example 2. Square a Binomial. Special Products of Binomials. Multiplying binomials to get difference of squares. Squaring a binomial. Multiplying expressions 0.5. Squaring a binomial example 2. Classic multiplying binomials video. Multiplying expressions 1. Factoring and the Distributive Property 3. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring and the Distributive Property. Factoring and the Distributive Property 2. Factor expressions using the GCF. Factoring quadratic expressions. Examples: Factoring simple quadratics. Example 1: Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring polynomials 1. Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor. Factoring polynomials 2. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Example: Basic grouping. Example 1: Factoring by grouping. Example 2: Factoring by grouping. Example 3: Factoring by grouping. Example 4: Factoring by grouping. Example 5: Factoring by grouping. Example 6: Factoring by grouping. Factoring polynomials by grouping. Factoring quadratics with two variables. Factoring quadratics with two variables example. Factoring polynomials with two variables. Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial. Interesting Polynomial Coefficient Problem. Polynomials1. Polynomials 2. Evaluating a polynomial at a given value. Simplify a polynomial. Adding Polynomials. Example: Adding polynomials with multiple variables. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 1. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 2. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 3. Subtracting Polynomials. Subtracting polynomials with multiple variables. Adding and subtracting polynomials. Multiplying Monomials by Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials 3. More multiplying polynomials. Multiplying polynomials. Polynomial Division. Polynomial divided by monomial. Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial. Dividing polynomials 1. Dividing polynomials with remainders. Synthetic Division. Synthetic Division Example 2. Why Synthetic Division Works. Factoring Sum of Cubes. Difference of Cubes Factoring. Algebraic Long Division. Algebra II: Simplifying Polynomials. Factoring Special Products. Example 1: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 1. Example 2: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 2. Factoring to produce difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 3. Example: Factoring perfect square trinomials. Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression. Example: Factoring special products. Multiplying Monomials. Dividing Monomials. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 1. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 2. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 3. Monomial Greatest Common Factor. Multiplying binomials word problem. FOIL for multiplying binomials. Multiplying Binomials with Radicals. Multiplying binomials example 1. FOIL method for multiplying binomials example 2. Square a Binomial. Special Products of Binomials. Multiplying binomials to get difference of squares. Squaring a binomial. Multiplying expressions 0.5. Squaring a binomial example 2. Classic multiplying binomials video. Multiplying expressions 1. Factoring and the Distributive Property 3. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring and the Distributive Property. Factoring and the Distributive Property 2. Factor expressions using the GCF. Factoring quadratic expressions. Examples: Factoring simple quadratics. Example 1: Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring polynomials 1. Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor. Factoring polynomials 2. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Example: Basic grouping. Example 1: Factoring by grouping. Example 2: Factoring by grouping. Example 3: Factoring by grouping. Example 4: Factoring by grouping. Example 5: Factoring by grouping. Example 6: Factoring by grouping. Factoring polynomials by grouping. Factoring quadratics with two variables. Factoring quadratics with two variables example. Factoring polynomials with two variables. Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial. Interesting Polynomial Coefficient Problem. Polynomials1. Polynomials 2. Evaluating a polynomial at a given value. Simplify a polynomial. Adding Polynomials. Example: Adding polynomials with multiple variables. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 1. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 2. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 3. Subtracting Polynomials. Subtracting polynomials with multiple variables. Adding and subtracting polynomials. Multiplying Monomials by Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials 3. More multiplying polynomials. Multiplying polynomials. Polynomial Division. Polynomial divided by monomial. Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial. Dividing polynomials 1. Dividing polynomials with remainders. Synthetic Division. Synthetic Division Example 2. Why Synthetic Division Works. Factoring Sum of Cubes. Difference of Cubes Factoring. Algebraic Long Division. Algebra II: Simplifying Polynomials.
Want to be an engineer or scientist? Lack mathematical confidence? Learn to think mathematically and explore essential concepts.
This course explains how you can use numbers to describe the natural world and make sense of everything from atoms to oceans.
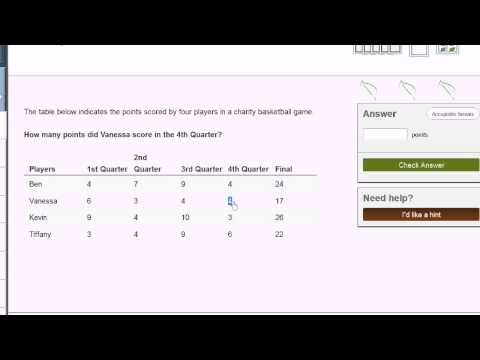
You already have many tools in your mathematical toolkit. In this topic, you'll use these in settings that you're likely to encounter in the real world!. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 2. Reading tables 2. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading Pictographs. Reading pictographs 1. Reading pictographs 2. Reading Bar Graphs. Histograms. Reading bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 3. Reading bar charts 3. Reading Line Graphs. Reading line charts 1. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Multistep word problems example 1). Multistep word problems example 2). Multistep word problems example 3). Multistep equations without variables. Greater than and less than symbols. Comparing whole numbers. Plotting inequalities on a number line. Writing numerical inequalities exercise. Writing numerical inequalities. Inequalities in one variable 1 exercise. Inequalities in one variable 1. Inequalities on a number line. Inequalities on a number line. Rational number word problem example 1. Rational number word problem example 2. Rational number word problem example 3. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Rational number word problems. Figuring out days of the week. Math patterns example 1. Math patterns example 2. Math patterns. Relationships between patterns. Interpreting relationships between patterns. Interpreting and graphing relationships between patterns. Visualizing and interpreting relationships between patterns. Constructing numerical expressions example. Evaluating an expression with and without parentheses. Expressions with parentheses. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 2. Reading tables 2. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading Pictographs. Reading pictographs 1. Reading pictographs 2. Reading Bar Graphs. Histograms. Reading bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 3. Reading bar charts 3. Reading Line Graphs. Reading line charts 1. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Multistep word problems example 1). Multistep word problems example 2). Multistep word problems example 3). Multistep equations without variables. Greater than and less than symbols. Comparing whole numbers. Plotting inequalities on a number line. Writing numerical inequalities exercise. Writing numerical inequalities. Inequalities in one variable 1 exercise. Inequalities in one variable 1. Inequalities on a number line. Inequalities on a number line. Rational number word problem example 1. Rational number word problem example 2. Rational number word problem example 3. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Rational number word problems. Figuring out days of the week. Math patterns example 1. Math patterns example 2. Math patterns. Relationships between patterns. Interpreting relationships between patterns. Interpreting and graphing relationships between patterns. Visualizing and interpreting relationships between patterns. Constructing numerical expressions example. Evaluating an expression with and without parentheses. Expressions with parentheses.
本课程以通俗的语言介绍粒子物理的主要内容和最前沿的研究。课程涉及的主要内容包括: 物质和反物质, 夸克和强相互作用,中微子和弱相互作用,对称性和它的作用, 粒子物理的标准模型,粒子天文学, 暗物质。 This course gives an brief introduction of the main content and the frontier of particle physics in popular language. It includes: matter and antimatter, quark and strong interaction, neutrino and weak interaction, symmetry and its applications, standard model of particle physics, particle astronomy, dark matter etc.
This course is taught in French Vous voulez comprendre l'arithmétique ? Vous souhaitez découvrir une application des mathématiques à la vie quotidienne ? Ce cours est fait pour vous ! De niveau première année d'université, vous apprendrez les bases de l'arithmétique (division euclidienne, théorème de Bézout, nombres premiers, congruence). Vous vous êtes déjà demandé comment sont sécurisées les transactions sur Internet ? Vous découvrirez les bases de la cryptographie, en commençant par les codes les plus simples pour aboutir au code RSA. Le code RSA est le code utilisé pour crypter les communications sur internet. Il est basé sur de l'arithmétique assez simple que l'on comprendra en détail. Vous pourrez en plus mettre en pratique vos connaissances par l'apprentissage de notions sur le langage de programmation Python. Vous travaillerez à l'aide de cours écrits et de vidéos, d'exercices corrigés en vidéos, des quiz, des travaux pratiques. Le cours est entièrement gratuit !
Methodisch ausgefeilter Doppel-MOOC mit Geometrie und Arithmetik. Du möchtest mathematisch denken lernen? Sei Kiebitz, Anpacker oder Formalisierer: Du hast die Wahl!
Teaches, as the antidote to rigor mortis, the art of educated guessing and opportunistic problem solving.
Calculus One is a first introduction to differential and integral calculus, emphasizing engaging examples from everyday life.
2003 AIME II Problem 1. 2003 AIME II Problem 3. Sum of factors of 27000. Sum of factors 2. 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 5. 2003 AIME II Problem 5 Minor Correction. Area Circumradius Formula Proof. 2003 AIME II Problem 6. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Sum of Polynomial Roots (Proof). Sum of Squares of Polynomial Roots. 2003 AIME II Problem 9. 2003 AIME II Problem 10. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 12. 2003 AIME II Problem 13. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 3). 2003 AIME II Problem 1. 2003 AIME II Problem 3. Sum of factors of 27000. Sum of factors 2. 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 5. 2003 AIME II Problem 5 Minor Correction. Area Circumradius Formula Proof. 2003 AIME II Problem 6. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Sum of Polynomial Roots (Proof). Sum of Squares of Polynomial Roots. 2003 AIME II Problem 9. 2003 AIME II Problem 10. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 12. 2003 AIME II Problem 13. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 3).
The AMC 10 is part of the series of contests administered by the MAA American Mathematics Competitions that determines the United States team in the International Math Olympiad. The AMC 10 is a 25 question, 75 minute multiple choice test for students in 10th grade or below. Two versions of the AMC 10 are offered each year. 2013 AMC 10 A #21 / AMC 12 A #17. 2013 AMC 10 A #22 / AMC 12 A #18. 2013 AMC 10 A #23 / AMC 12 A #19. 2013 AMC 10 A #24. 2013 AMC 10 A #25. 2013 AMC 10 A #21 / AMC 12 A #17. 2013 AMC 10 A #22 / AMC 12 A #18. 2013 AMC 10 A #23 / AMC 12 A #19. 2013 AMC 10 A #24. 2013 AMC 10 A #25.
This course is designed for students who will be starting or restarting college within the next year, and for current students who have not completed their general education math requirement. It will provide math refresher materials covering a wide range of mathematical concepts together with information about success in college. Incoming college students are typically placed in college math courses based on placement exam scores. Students often take these placement exams with minimal preparation or after a long break since their last math class. The study materials in the course will help students prepare for placement exams, and higher scores mean fewer required math courses in college. Students who have already taken a placement exam (such as the ACT) can also use these materials to study and then retest, hopefully scoring higher. College students who have started, but not finished their math courses, can also retake a placement exam and possibly skip a math class. The course will also be valuable for anyone who just wants to refresh their math skills. The provided study materials are individualized based on a student’s current knowledge. Each student will be provided a customized learning path that maximizes efficiency so that study time is spent where it’s needed most. Beyond math content, the course will also provide college success material such as test-taking strategies, new student orientation, and study techniques. All of this material can be accessed separately from the math content so even if a student is already placed highly in math, or has tested out of it completely, the course will provide valuable information to help the student orient to college and to get the most out of the college experience.
Real Analysis II is the sequel to Saylor’s Real Analysis I, and together these two courses constitute the foundations of real analysis in mathematics. In this course, you will build on key concepts presented in Real Analysis I, particularly the study of the real number system and real-valued functions defined on all or part (usually intervals) of the real number line. The main objective of MA241 [1] was to introduce you to the concept and theory of differential and integral calculus as well as the mathematical analysis techniques that allow us to understand and solve various problems at the heart of sciencenamely, questions in the fields of physics, economics, chemistry, biology, and engineering. In this course, you will build on these techniques with the goal of applying them to the solution of more complex mathematical problems. As long as a problem can be modeled as a functional relation between two quantities, each of which can be expressed as a set of real numbers, the techniques used for real-value…
This course provides an introduction to causal and statistical reasoning. After taking this course, students will be better prepared to make rational decisions about their own lives and about matters of social policy. They will be able to assess criticallyeven if informallyclaims that they encounter during discussions or when considering a news article or report. A variety of materials are presented, including Case Studies where students are given the opportunity to examine a causal claim, and the Causality Lab, a virtual environment to simulate the science of causal discovery. Students have frequent opportunities to check their understanding and practice their skills. This course is meant to serve students in several situations. One, it is meant for students who will only take one such research methods course, and are interested in gaining basic skills that will help them to think critically about claims they come across in their daily lives, such as through a news article. Two, it is meant for students who will take a few statistics courses in service of a related field of study. Three, it is meant for students interested in the foundations of quantitative causal models: called Bayes Networks.
Ganz gleich in welcher Wissenschaftsdisziplin, Statistik ist das Schweizer Armeemesser für die Behandlung von vielen Zahlen – um daraus wenige Zahlen zu machen. Das klingt unspektakulär, hat aber schon so manchen Studierenden der Human-, Wirtschafts- und Naturwissenschaften an den Rand der Verzweiflung geführt. Dabei ist Statistik überall, in den alltäglichsten Situationen und den komplexesten Forschungsfragen.
In dieser Einführung kümmern wir uns um das Fundament der Statistik, die Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie. Das klingt schlimm, ist es aber nicht. Wir erfahren etwas über die männliche Sicht weiblichen Intellekts, antike Cassettenhüllen, gezinkte Würfel, Milchreis, Hochrisiko-Sportfeste und vieles mehr, das uns den Einstieg in die Welt der Wahrscheinlichkeit so leicht macht als sei die Statistik auf eine strenge Diät gegangen.
Kursüberblick
Der Kurs beschäftigt sich mit Inhalten rund um das Gebiet der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung. Ausgehend von verschiedene Definitionen für Wahrscheinlichkeit widmen wir uns schnell den praxisnäheren Fragen, die mit Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung beantwortet werden können. Wir erfahren den Unterschied zwischen Häufigkeit und Wahrscheinlichkeit, lernen den Satz von Bayes kennen und danach direkt Bernoullis Zufallsexperimente. Diese bringen uns zu den diskreten Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen, von denen wir die Binomialverteilung, die Poissonverteilung und die Hypergeometrische Verteilung näher kennenlernen werden. Danach kümmern wir uns um stetige Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen und deren wichtigsten Vertreter, die Normalverteilung. Links liegen lassen wir während des ganzen Kurses die von Vielen gefürchtete Kombinatorik, die wir nur an zwei Stellen wirklich benötigen.
Lernergebnisse
Am Ende des Kurses wirst Du die grundlegenden formalen Elemente der Wahrscheinlichkeit kennen. Du wirst verstanden haben, was sich Pierre Simon Laplace und Nikolaj Kolmogoroff unter dem Begriff Wahrscheinlichkeit vorgestellt haben. Du wirst mit bedingten Wahrscheinlichkeiten und dem Satz von Bayes umgehen können. Und schließlich wirst Du Dich in vielen Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen zurechtfinden wie der Binomialverteilung, der Poissonverteilung, der hypergeometrischen Verteilung und der Normalverteilung.
Vorkenntnisse
Alles, was Du zum Genuss der Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie brauchst, lernst Du hier. Du brauchst keine besonderen Vorkenntnisse, denn mehr als Plus, Minus, Mal und Geteilt wird hier kaum gerechnet. Versprochen! Also schau vorbei und lern mit uns die Statistik von einer ganz neuen Seite kennen.
FAQ
Für grundsätzliche Fragen findest du hier die FAQs.
Course Summary
Modelling and simulation make a particular part of the world easier to define, visualize and understand. Both require the identification of relevant aspects of a situation in the real world and then the use of different types of models for different objectives and the definition of the most suitable model parameters.
This course provides to you a number of methods suitable for modelling technical systems and processes in a wide range of applications. These applications cover a range from image processing via machine learning to face recognition.
After introducing the techniques in general, you train their application to real problems employing the widely used modelling and simulation tool MATLAB®.
What will I learn?
- You will be acquainted with the concepts of modelling and simulation
- You will be able to implement and simulate models using MATLAB®.
- You will acquire further knowledge of Image Processing, Optical Character Recognition, Machine Learning and Face Recognition.
- If you are an enthusiastic student with only rudimentary programming knowledge you can acquire an understanding of basic MATLAB® programming.
What do I have to know?
The course will be taught on an academic level for undergraduate students. Therefore, mathematics and physics knowledge of at least secondary education level as well as programming knowledge is a prerequisite. MATLAB® is commercial software. As a result of support from MathWorks, students will be granted a downloadable license to MATLAB® for the duration of the course.
Course Schedule
Chapter 1: Introduction to MATLAB Concepts
Chapter 2: Modelling and Simulation
Chapter 3: The Basic Problem Solving Toolbox
Chapter 4: Advanced Problem Solving Methods
Chapter 5: Statistics and Image Processing
Chapter 6: Machine Learning in a Nutshell
Chapter 7: Optical Character Recognition
Cahpter 8: Face Recognition
This class covers the analysis and modeling of stochastic processes. Topics include measure theoretic probability, martingales, filtration, and stopping theorems, elements of large deviations theory, Brownian motion and reflected Brownian motion, stochastic integration and Ito calculus and functional limit theorems. In addition, the class will go over some applications to finance theory, insurance, queueing and inventory models.
Build your earth science vocabulary and learn about cycles of matter and types of sedimentary rocks through the Education Portal course Earth Science 101: Earth Science. Our series of video lessons and accompanying self-assessment quizzes can help you boost your scientific knowledge ahead of the Excelsior Earth Science exam . This course was designed by experienced educators and examines both science basics, like experimental design and systems of measurement, and more advanced topics, such as analysis of rock deformation and theories of continental drift.
Build your earth science vocabulary and learn about cycles of matter and types of sedimentary rocks through the Education Portal course Earth Science 101: Earth Science. Our series of video lessons and accompanying self-assessment quizzes can help you boost your scientific knowledge ahead of the Excelsior Earth Science exam . This course was designed by experienced educators and examines both science basics, like experimental design and systems of measurement, and more advanced topics, such as analysis of rock deformation and theories of continental drift.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.