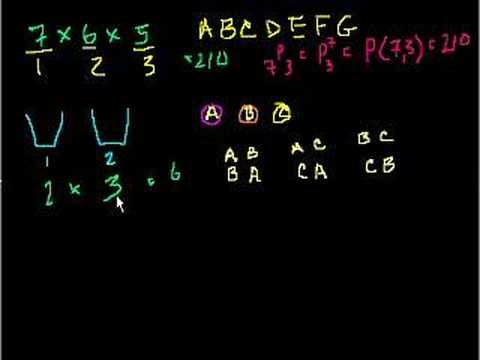Online courses directory (418)
Understanding and solving exponents without algebra. Introduction to exponents. Raising a number to the 0th and 1st power. Powers of 1 and -1. Powers of fractions. Powers of zero. Exponent example 1. Exponent example 2. Positive and zero exponents. Understanding Square Roots. Square roots of perfect squares. Approximating Square Roots. Estimating square roots. Simplifying square roots. Simplifying radicals. Square Roots and Real Numbers. Simplifying radicals. Simplifying radicals 2. Adding and simplifying radicals. Adding and subtracting radicals. Finding Cube Roots. Cube root of a non-perfect cube. Simplifying a cube root. Cube roots. Cube roots 2. Patterns in zeros exercise. Patterns in zeros. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties Involving Quotients. Exponent rules. Negative exponents. Negative Exponent Intuition. Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents. Negative exponents. Basic fractional exponents. Negative fractional exponent examples. Negative fractional exponent examples 2. Fractional exponents. Fractional exponents with numerators other than 1. Fractional exponents 2. Introduction to scientific notation. Scientific Notation. Scientific notation intuition. Scientific Notation Examples. Scientific Notation I. Scientific Notation Example 2. Scientific notation. Orders of magnitude exercise example 1. Orders of magnitude exercise example 2. Orders of magnitude. Multiplying in Scientific Notation. Multiplying in scientific notation example. Dividing in scientific notation example. Multiplying and dividing in scientific notation. Multiplying and dividing scientific notation. Simplifying a complicated expression into scientific notation. Calculating red blood cells in the body using scientific notation. Computing in scientific notation. Introduction to exponents. Raising a number to the 0th and 1st power. Powers of 1 and -1. Powers of fractions. Powers of zero. Exponent example 1. Exponent example 2. Positive and zero exponents. Understanding Square Roots. Square roots of perfect squares. Approximating Square Roots. Estimating square roots. Simplifying square roots. Simplifying radicals. Square Roots and Real Numbers. Simplifying radicals. Simplifying radicals 2. Adding and simplifying radicals. Adding and subtracting radicals. Finding Cube Roots. Cube root of a non-perfect cube. Simplifying a cube root. Cube roots. Cube roots 2. Patterns in zeros exercise. Patterns in zeros. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties Involving Quotients. Exponent rules. Negative exponents. Negative Exponent Intuition. Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents. Negative exponents. Basic fractional exponents. Negative fractional exponent examples. Negative fractional exponent examples 2. Fractional exponents. Fractional exponents with numerators other than 1. Fractional exponents 2. Introduction to scientific notation. Scientific Notation. Scientific notation intuition. Scientific Notation Examples. Scientific Notation I. Scientific Notation Example 2. Scientific notation. Orders of magnitude exercise example 1. Orders of magnitude exercise example 2. Orders of magnitude. Multiplying in Scientific Notation. Multiplying in scientific notation example. Dividing in scientific notation example. Multiplying and dividing in scientific notation. Multiplying and dividing scientific notation. Simplifying a complicated expression into scientific notation. Calculating red blood cells in the body using scientific notation. Computing in scientific notation.
Understanding decimals conceptually, using operations with decimals, rounding and estimating with decimals, and converting decimals. Decimal Place Value. Decimal Place Value 2. Writing out a decimal in words. Expanding out a decimal by place value. Writing a decimal to represent a quantity. Writing and interpreting decimals. Comparing place values in decimals. Comparing decimal place value. Using money to understand decimal place value. Money and decimal place value intuition. Regrouping with decimals. Regrouping with decimals example. Regrouping decimals example 2. Regrouping decimals. Decimals on a Number Line. Decimals on the number line 1. Points on a number line. Decimals on the number line 2. Positive and negative decimals on a number line. Decimals on the number line 3. Comparing decimals example 1. Comparing decimals example 2. Comparing decimals 1. Comparing decimals example 3. Comparing decimals example 4. Comparing decimals 2. Adding decimals example 1. Adding decimals example 2. Adding decimals example 3. Adding decimals 0.5. Adding decimals 1. Adding decimals 2. Subtracting Decimals. Subtracting decimals 0.5. Subtracting decimals. Adding decimals word problem. Subtracting Decimals Word Problem. Adding and subtracting decimals word problems. Subtracting decimals (old). Multiplying Decimals. Multiplying decimals example 2. Multiple examples multiplying decimals. Multiplying decimals. Dividing completely to get decimal answer. Dividing completely to get decimal answer example 2. Dividing completely. Dividing a decimal by a whole number. Dividing decimals 1. Dividing a whole number by a decimal. Dividing decimals 2. Dividing Decimals. Dividing decimal. Dividing decimals. Converting fractions to decimals (ex1). Converting fractions to decimals (ex2). Converting fractions to decimals. Converting Fractions to Decimals Example. Converting fractions to decimals. Decimals and Fractions. Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 1). Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 2). Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 3). Converting decimals to fractions 1. Converting decimals to fractions 2 (ex 1). Converting decimals to fractions 2 (ex 2). Converting decimals to fractions 2. Describing the Meaning of Percent. Describing the Meaning of Percent 2. Representing a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Converting decimals to percents (ex 1). Converting decimals to percents (ex 2). Converting decimals to percents. Converting percents to decimals (ex 1). Converting percents to decimals (ex 2). Converting percents to decimals. Finding percentages example. Percent word problems. Taking a percentage example. Finding percents. Identifying Percent Amount and Base. Representing a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction 2. Ordering numeric expressions. Growing by a percentage. Solving Percent Problems. Solving Percent Problems 2. Solving Percent Problems 3. Discount tax and tip word problems. Markup and commission word problems. Rounding Decimals. Rounding numbers. Estimation with Decimals. Estimation with decimals. Significant Figures. More on Significant Figures. Addition and Subtraction with Significant Figures. Multiplying and Dividing with Significant Figures. Significant figures. Multiplying a Decimal by a Power of 10. Dividing a Decimal by a Power of 10. Dividing a decimal by a power of 10 (part 2). Understanding moving the decimal. Fractions as division by a power of 10. Adding and subtracting a decimal percentage and fraction. Adding fractions decimals and percentages. Adding and subtracting three fractions. Adding and subtracting rational numbers. Decimal Place Value. Decimal Place Value 2. Writing out a decimal in words. Expanding out a decimal by place value. Writing a decimal to represent a quantity. Writing and interpreting decimals. Comparing place values in decimals. Comparing decimal place value. Using money to understand decimal place value. Money and decimal place value intuition. Regrouping with decimals. Regrouping with decimals example. Regrouping decimals example 2. Regrouping decimals. Decimals on a Number Line. Decimals on the number line 1. Points on a number line. Decimals on the number line 2. Positive and negative decimals on a number line. Decimals on the number line 3. Comparing decimals example 1. Comparing decimals example 2. Comparing decimals 1. Comparing decimals example 3. Comparing decimals example 4. Comparing decimals 2. Adding decimals example 1. Adding decimals example 2. Adding decimals example 3. Adding decimals 0.5. Adding decimals 1. Adding decimals 2. Subtracting Decimals. Subtracting decimals 0.5. Subtracting decimals. Adding decimals word problem. Subtracting Decimals Word Problem. Adding and subtracting decimals word problems. Subtracting decimals (old). Multiplying Decimals. Multiplying decimals example 2. Multiple examples multiplying decimals. Multiplying decimals. Dividing completely to get decimal answer. Dividing completely to get decimal answer example 2. Dividing completely. Dividing a decimal by a whole number. Dividing decimals 1. Dividing a whole number by a decimal. Dividing decimals 2. Dividing Decimals. Dividing decimal. Dividing decimals. Converting fractions to decimals (ex1). Converting fractions to decimals (ex2). Converting fractions to decimals. Converting Fractions to Decimals Example. Converting fractions to decimals. Decimals and Fractions. Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 1). Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 2). Converting decimals to fractions 1 (ex 3). Converting decimals to fractions 1. Converting decimals to fractions 2 (ex 1). Converting decimals to fractions 2 (ex 2). Converting decimals to fractions 2. Describing the Meaning of Percent. Describing the Meaning of Percent 2. Representing a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Converting decimals to percents (ex 1). Converting decimals to percents (ex 2). Converting decimals to percents. Converting percents to decimals (ex 1). Converting percents to decimals (ex 2). Converting percents to decimals. Finding percentages example. Percent word problems. Taking a percentage example. Finding percents. Identifying Percent Amount and Base. Representing a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction 2. Ordering numeric expressions. Growing by a percentage. Solving Percent Problems. Solving Percent Problems 2. Solving Percent Problems 3. Discount tax and tip word problems. Markup and commission word problems. Rounding Decimals. Rounding numbers. Estimation with Decimals. Estimation with decimals. Significant Figures. More on Significant Figures. Addition and Subtraction with Significant Figures. Multiplying and Dividing with Significant Figures. Significant figures. Multiplying a Decimal by a Power of 10. Dividing a Decimal by a Power of 10. Dividing a decimal by a power of 10 (part 2). Understanding moving the decimal. Fractions as division by a power of 10. Adding and subtracting a decimal percentage and fraction. Adding fractions decimals and percentages. Adding and subtracting three fractions. Adding and subtracting rational numbers.
Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used). Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used).
Triangles are not always right (although they are never wrong), but when they are it opens up an exciting world of possibilities. Not only are right triangles cool in their own right (pun intended), they are the basis of very important ideas in analytic geometry (the distance between two points in space) and trigonometry. Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean Theorem 1. Pythagorean Theorem 2. Pythagorean Theorem 3. Pythagorean theorem. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem II. Garfield's proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. Bhaskara's proof of Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem Proof Using Similarity. Another Pythagorean Theorem Proof. 30-60-90 Triangle Side Ratios Proof. 45-45-90 Triangle Side Ratios. 30-60-90 Triangle Example Problem. Special right triangles. Area of a Regular Hexagon. 45-45-90 Triangles. Intro to 30-60-90 Triangles. 30-60-90 Triangles II. Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean Theorem 1. Pythagorean Theorem 2. Pythagorean Theorem 3. Pythagorean theorem. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem II. Garfield's proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. Bhaskara's proof of Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem Proof Using Similarity. Another Pythagorean Theorem Proof. 30-60-90 Triangle Side Ratios Proof. 45-45-90 Triangle Side Ratios. 30-60-90 Triangle Example Problem. Special right triangles. Area of a Regular Hexagon. 45-45-90 Triangles. Intro to 30-60-90 Triangles. 30-60-90 Triangles II.
Solving exponential and radical expressions and equations. Using scientific notation and significant figures. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations.
Extending our understanding of numbers below 0. Thinking about "absolute" distance from 0. Negative Numbers Introduction. Negative numbers on the number line. Number line 3. Ordering Negative Numbers. Ordering negative numbers. Number opposites. Number opposites. Negative Numbers Introduction. Number opposites. Example: Adding negative numbers. Example: Adding integers with different signs. Adding negative numbers. Adding and subtracting negative number examples. Why Subtracting a Negative Equivalent to Adding a Positive. Adding and subtracting negative numbers. Negative number word problems 1. Negative number word problems. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Adding/Subtracting negative numbers. Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers. Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive. Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes Intuitive Sense. Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers. Example: Multiplying numbers with different signs. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Absolute Value and Number Lines. Absolute Value 1. Finding absolute values. Absolute Value of Integers. Comparing Absolute Values. Comparing absolute values. Absolute value word problems exercise. Absolute value word problems. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Negative Numbers Introduction. Negative numbers on the number line. Number line 3. Ordering Negative Numbers. Ordering negative numbers. Number opposites. Number opposites. Negative Numbers Introduction. Number opposites. Example: Adding negative numbers. Example: Adding integers with different signs. Adding negative numbers. Adding and subtracting negative number examples. Why Subtracting a Negative Equivalent to Adding a Positive. Adding and subtracting negative numbers. Negative number word problems 1. Negative number word problems. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Adding/Subtracting negative numbers. Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers. Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive. Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes Intuitive Sense. Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers. Example: Multiplying numbers with different signs. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Absolute Value and Number Lines. Absolute Value 1. Finding absolute values. Absolute Value of Integers. Comparing Absolute Values. Comparing absolute values. Absolute value word problems exercise. Absolute value word problems. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Constructing and interpreting absolute value.
Exploring a world where both sides aren't equal anymore!. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1.
This topic introduces the basic conceptual tools that underpin our journey through Euclidean geometry. These include the ideas of points, lines, line segments, rays, and planes. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment.
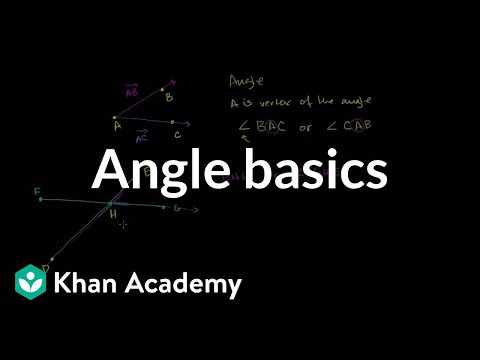
This topic continues our journey through the world of Euclid by helping us understand angles and how they can relate to each other. Angle basics. Measuring angles in degrees. Using a protractor. Measuring angles. Measuring angles. Acute right and obtuse angles. Angle types. Vertical, adjacent and linearly paired angles. Exploring angle pairs. Introduction to vertical angles. Vertical angles. Using algebra to find the measures of vertical angles. Vertical angles 2. Proof-Vertical Angles are Equal. Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals. Identifying Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Figuring out angles between transversal and parallel lines. Congruent angles. Parallel lines 1. Using algebra to find measures of angles formed from transversal. Parallel lines 2. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. Proof - Sum of Measures of Angles in a Triangle are 180. Triangle Angle Example 1. Triangle Angle Example 2. Triangle Angle Example 3. Challenging Triangle Angle Problem. Proof - Corresponding Angle Equivalence Implies Parallel Lines. Finding more angles. Angles 1. Angles 2. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Angles of a polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Introduction to angles (old). Angles (part 2). Angles (part 3). Angles formed between transversals and parallel lines. Angles of parallel lines 2. The Angle Game. Angle Game (part 2). Acute right and obtuse angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of complementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of supplementary angles. Angle addition postulate. Angle basics. Measuring angles in degrees. Using a protractor. Measuring angles. Measuring angles. Acute right and obtuse angles. Angle types. Vertical, adjacent and linearly paired angles. Exploring angle pairs. Introduction to vertical angles. Vertical angles. Using algebra to find the measures of vertical angles. Vertical angles 2. Proof-Vertical Angles are Equal. Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals. Identifying Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Figuring out angles between transversal and parallel lines. Congruent angles. Parallel lines 1. Using algebra to find measures of angles formed from transversal. Parallel lines 2. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. Proof - Sum of Measures of Angles in a Triangle are 180. Triangle Angle Example 1. Triangle Angle Example 2. Triangle Angle Example 3. Challenging Triangle Angle Problem. Proof - Corresponding Angle Equivalence Implies Parallel Lines. Finding more angles. Angles 1. Angles 2. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Angles of a polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Introduction to angles (old). Angles (part 2). Angles (part 3). Angles formed between transversals and parallel lines. Angles of parallel lines 2. The Angle Game. Angle Game (part 2). Acute right and obtuse angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of complementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of supplementary angles. Angle addition postulate.
You have probably been wondering whether our powers of algebraic problem solving break down if we divide by the variable or we have entire expressions in denominator of a fraction. Well, they don't! In this topic, you'll learn how to interpret and manipulate rational expressions (when you have one algebraic expression divided by another)!. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Simplifying Rational Expressions 1. Dividing polynomials by binomials 1. Simplifying Rational Expressions 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 2. Simplifying rational expressions 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions 3. Simplifying Rational Expressions Example 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 3. Simplifying rational expressions 3. Simplifying rational expressions 4. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 2. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 3. Subtracting Rational Expressions. Simplifying First for Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 0.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3. Multiplying and Simplifying Rational Expressions. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 4. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 5. Rationalizing Denominators of Expressions. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Partial Fraction Expansion 1. Partial Fraction Expansion 2. Partial Fraction Expansion 3. Partial fraction expansion. Ex 1 Multi step equation. Solving rational equations 1. Rational Equations. Solving Rational Equations 1. Solving Rational Equations 2. Solving Rational Equations 3. Applying Rational Equations 1. Applying Rational Equations 2. Applying Rational Equations 3. Solving rational equations 2. Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations. Extraneous solutions. Rational Inequalities. Rational Inequalities 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Simplifying Rational Expressions 1. Dividing polynomials by binomials 1. Simplifying Rational Expressions 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 2. Simplifying rational expressions 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions 3. Simplifying Rational Expressions Example 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 3. Simplifying rational expressions 3. Simplifying rational expressions 4. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 2. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 3. Subtracting Rational Expressions. Simplifying First for Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 0.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3. Multiplying and Simplifying Rational Expressions. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 4. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 5. Rationalizing Denominators of Expressions. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Partial Fraction Expansion 1. Partial Fraction Expansion 2. Partial Fraction Expansion 3. Partial fraction expansion. Ex 1 Multi step equation. Solving rational equations 1. Rational Equations. Solving Rational Equations 1. Solving Rational Equations 2. Solving Rational Equations 3. Applying Rational Equations 1. Applying Rational Equations 2. Applying Rational Equations 3. Solving rational equations 2. Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations. Extraneous solutions. Rational Inequalities. Rational Inequalities 2.
Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Expressing ratios as fractions. Describing ratios exercise. Describing ratios. Ratio word problem exercise example 1. Ratio word problem exercise example 2. Ratio word problems. Proportion validity example. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 2. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 3. Solving ratio problems with tables. Usain Bolt's Average Speed. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Rate problems 0.5. Multiple rates word problem. Rate problems 2. Converting pounds to ounces. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting Yards into Inches. Performing arithmetic calculations on units of volume. Application problems involving units of weight. Solving application problems involving units of volume. Gas cost for a roadtrip. Squirrel survival. Converting units of length. Unit Conversion Example: Drug Dosage. Unit Conversion with Fractions. Units. Speed translation. Unit conversion within the metric system. Converting within the metric system. Perimeter and Unit Conversion. Applying the Metric System. Conversion between metric units. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales. Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Expressing ratios as fractions. Describing ratios exercise. Describing ratios. Ratio word problem exercise example 1. Ratio word problem exercise example 2. Ratio word problems. Proportion validity example. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 2. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 3. Solving ratio problems with tables. Usain Bolt's Average Speed. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Rate problems 0.5. Multiple rates word problem. Rate problems 2. Converting pounds to ounces. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting Yards into Inches. Performing arithmetic calculations on units of volume. Application problems involving units of weight. Solving application problems involving units of volume. Gas cost for a roadtrip. Squirrel survival. Converting units of length. Unit Conversion Example: Drug Dosage. Unit Conversion with Fractions. Units. Speed translation. Unit conversion within the metric system. Converting within the metric system. Perimeter and Unit Conversion. Applying the Metric System. Conversion between metric units. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales.
Permutations and combinations. Using combinatorics to solve questions in probability. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations.
Measures of central tendency and dispersion. Mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance.
This tutorial is the meat of much of classical physics. We think about what a force is and how Newton changed the world's (and possibly your) view of how reality works. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face.
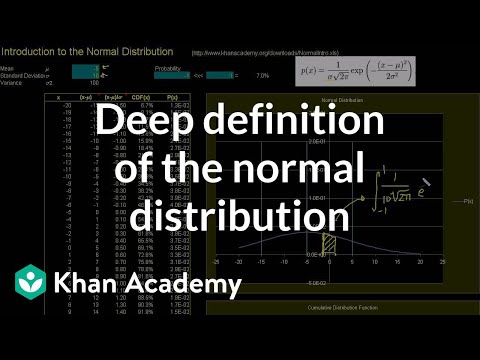
Making inferences based on sample data. Confidence intervals. Margin of error. Hypothesis testing. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic.
Understanding how we can map one set of vectors to another set. Matrices used to define linear transformations. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible.
We explore creating and moving between various coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems.
Linear differential equations that contain second derivatives. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4.
Throughout this course, we will use algebra to quantify and describe the world around us. Have you ever wondered how many songs can fit onto your flash drive? By the end of the course, you’ll have stronger skills for modeling problems, analyzing patterns, and using algebra to arrive at conclusions.
Sample questions from the A.P. Calculus AB and BC exams (both multiple choice and free answer). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1 parts b c d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (c & d). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (c). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4c. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5c.. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 a. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 b&c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 c&d. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 d. Calculus BC 2008 2 a. Calculus BC 2008 2 b &c. Calculus BC 2008 2d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6c. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1 parts b c d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (c & d). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (c). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4c. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5c.. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 a. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 b&c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 c&d. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 d. Calculus BC 2008 2 a. Calculus BC 2008 2 b &c. Calculus BC 2008 2d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6c. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6d.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.