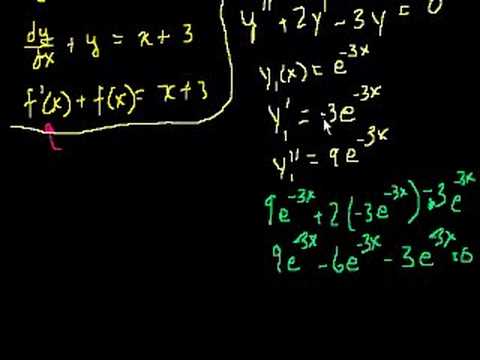Courses tagged with "Customer Service Certification Program" (283)
Topics covered in a first year course in differential equations. Need to understand basic differentiation and integration from Calculus playlist before starting here. What is a differential equation. Separable Differential Equations. Separable differential equations 2. Exact Equations Intuition 1 (proofy). Exact Equations Intuition 2 (proofy). Exact Equations Example 1. Exact Equations Example 2. Exact Equations Example 3. Integrating factors 1. Integrating factors 2. First order homegenous equations. First order homogeneous equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4. Laplace Transform 1. Laplace Transform 2. Laplace Transform 3 (L{sin(at)}). Laplace Transform 4. Laplace Transform 5. Laplace Transform 6. Laplace Transform to solve an equation. Laplace Transform solves an equation 2. More Laplace Transform tools. Using the Laplace Transform to solve a nonhomogeneous eq. Laplace Transform of : L{t}. Laplace Transform of t^n: L{t^n}. Laplace Transform of the Unit Step Function. Inverse Laplace Examples. Laplace/Step Function Differential Equation. Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform of the Dirac Delta Function. Introduction to the Convolution. The Convolution and the Laplace Transform. Using the Convolution Theorem to Solve an Initial Value Prob.
This introductory calculus course covers differentiation and integration of functions of one variable, with applications.
Select problems from ck12.org's Algebra 1 FlexBook (Open Source Textbook). This is a good playlist to review if you want to make sure you have a good understanding of all of the major topics in Algebra I. Variable Expressions. Order of Operations Example. Patterns and Equations. Equations and Inequalities. Domain and Range of a Function. Functions as Graphs. Word Problem Solving Plan 1. Word Problem Solving Strategies. Integers and Rational Numbers. Addition of Rational Numbers. Subtraction of Rational Numbers. Multiplication of Rational Numbers. Distributive Property Example 1. Division of Rational Numbers. Square Roots and Real Numbers. Problem Solving Word Problems 2. One Step Equations. Two-Step Equations. Ex 1: Distributive property to simplify . Ex 3: Distributive property to simplify . Ratio and Proportion. Scale and Indirect Measurement. Percent Problems. Another percent example. The Coordinate Plane. Graphing Using Intercepts. Graphs of Linear Equations. Slope and Rate of Change. Graphs Using Slope-Intercept Form. Direct Variation Models. Function example problems. Word Problem Solving 4. Linear Equations in Slope Intercept Form. Linear Equations in Point Slope Form. Linear Equations in Standard Form. Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Fitting a Line to Data. Predicting with Linear Models. Using a Linear Model. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. Compound Inequalities. Absolute Value Equations. Absolute Value Inequalities. Graphing Inequalities. Solving Linear Systems by Graphing. Solving Linear Systems by Substitution. Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination. Solving Systems of Equations by Multiplication. Special Types of Linear Systems. Systems of Linear Inequalities. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Exponent Properties Involving Quotients. Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents. Scientific Notation. Exponential Growth Functions. Exponential Decay Functions. Geometric Sequences (Introduction). Word Problem Solving- Exponential Growth and Decay. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Multiplication of Polynomials. Special Products of Binomials. Polynomial Equations in Factored Form. Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring Special Products. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Graphs of Quadratic Functions. Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing. Solving Quadratic Equations by Square Roots. Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square. How to Use the Quadratic Formula. Proof of Quadratic Formula. Discriminant of Quadratic Equations. Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models. Identifying Quadratic Models. Identifying Exponential Models. Quadratic Regression. Shifting functions. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. More Simplifying Radical Expressions. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Radical Equation Examples. More Involved Radical Equation Example. Pythagorean Theorem. Distance Formula. Midpoint Formula. Visual Pythagorean Theorem Proof. Average or Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean, Median, and Mode. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Stem and Leaf Plots. Histograms. Box-and-whisker Plot. Proportionality. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Polynomial Division. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions. Adding Rational Expressions Example 1. Adding Rational Expressions Example 2. Adding Rational Expressions Example 3. Solving Rational Equations. Two more examples of solving rational equations. Surveys and Samples.
Non-trigonometry pre-calculus topics. Solid understanding of all of the topics in the "Algebra" playlist should make this playlist pretty digestible. Introduction to Limits (HD). Introduction to Limits. Limit Examples (part 1). Limit Examples (part 2). Limit Examples (part3). Limit Examples w/ brain malfunction on first prob (part 4). Squeeze Theorem. Proof: lim (sin x)/x. More Limits. Sequences and Series (part 1). Sequences and series (part 2). Permutations. Combinations. Binomial Theorem (part 1). Binomial Theorem (part 2). Binomial Theorem (part 3). Introduction to interest. Interest (part 2). Introduction to compound interest and e. Compound Interest and e (part 2). Compound Interest and e (part 3). Compound Interest and e (part 4). Exponential Growth. Polar Coordinates 1. Polar Coordinates 2. Polar Coordinates 3. Parametric Equations 1. Parametric Equations 2. Parametric Equations 3. Parametric Equations 4. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Basic Complex Analysis. Exponential form to find complex roots. Complex Conjugates. Series Sum Example. Complex Determinant Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Logarithmic Scale. Vi and Sal Explore How We Think About Scale. Vi and Sal Talk About the Mysteries of Benford's Law. Benford's Law Explanation (Sequel to Mysteries of Benford's Law).
This is a variation on 18.02 Multivariable Calculus. It covers the same topics as in 18.02, but with more focus on mathematical concepts.
Acknowledgement
Prof. McKernan would like to acknowledge the contributions of Lars Hesselholt to the development of this course.
Differential Equations are the language in which the laws of nature are expressed. Understanding properties of solutions of differential equations is fundamental to much of contemporary science and engineering. Ordinary differential equations (ODE's) deal with functions of one variable, which can often be thought of as time.
This course analyzes the functions of a complex variable and the calculus of residues. It also covers subjects such as ordinary differential equations, partial differential equations, Bessel and Legendre functions, and the Sturm-Liouville theory.
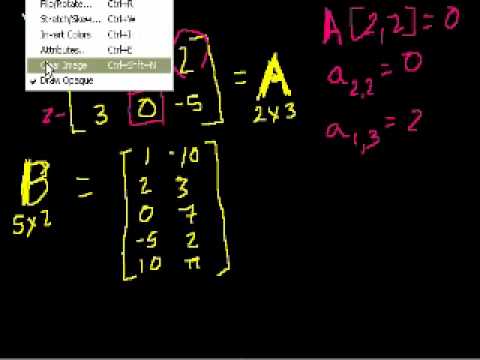
Matrices, vectors, vector spaces, transformations. Covers all topics in a first year college linear algebra course. This is an advanced course normally taken by science or engineering majors after taking at least two semesters of calculus (although calculus really isn't a prereq) so don't confuse this with regular high school algebra. Introduction to matrices. Matrix multiplication (part 1). Matrix multiplication (part 2). Idea Behind Inverting a 2x2 Matrix. Inverting matrices (part 2). Inverting Matrices (part 3). Matrices to solve a system of equations. Matrices to solve a vector combination problem. Singular Matrices. 3-variable linear equations (part 1). Solving 3 Equations with 3 Unknowns. Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A). A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Orthogonal Complements. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes.
This course continues from Analysis I (18.100B), in the direction of manifolds and global analysis. The first half of the course covers multivariable calculus. The rest of the course covers the theory of differential forms in n-dimensional vector spaces and manifolds.
This is a undergraduate course. It will cover normed spaces, completeness, functionals, Hahn-Banach theorem, duality, operators; Lebesgue measure, measurable functions, integrability, completeness of L-p spaces; Hilbert space; compact, Hilbert-Schmidt and trace class operators; as well as spectral theorem.
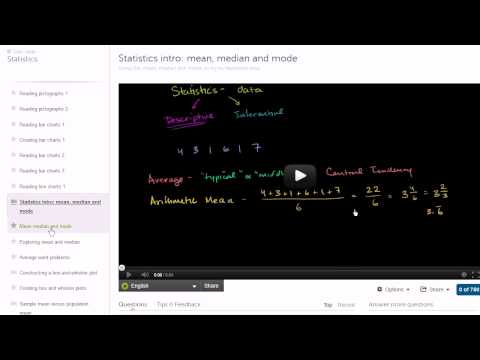
Introduction to statistics. We start with the basics of reading and interpretting data and then build into descriptive and inferential statistics that are typically covered in an introductory course on the subject. Overview of Khan Academy statistics. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Sample mean versus population mean.. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Introduction to Random Variables. Probability Density Functions. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value: E(X). Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. Law of Large Numbers. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Type 1 Errors. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line. Correlation and Causality. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Mean Median and Mode. Range and Mid-range. Reading Pictographs. Reading Bar Graphs. Reading Line Graphs. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance. Deductive Reasoning 1. Deductive Reasoning 2. Deductive Reasoning 3. Inductive Reasoning 1. Inductive Reasoning 2. Inductive Reasoning 3. Inductive Patterns.
Wavelets are localized basis functions, good for representing short-time events. The coefficients at each scale are filtered and subsampled to give coefficients at the next scale. This is Mallat's pyramid algorithm for multiresolution, connecting wavelets to filter banks. Wavelets and multiscale algorithms for compression and signal/image processing are developed. Subject is project-based for engineering and scientific applications.
This graduate-level course focuses on current research topics in computational complexity theory. Topics include: Nondeterministic, alternating, probabilistic, and parallel computation models; Boolean circuits; Complexity classes and complete sets; The polynomial-time hierarchy; Interactive proof systems; Relativization; Definitions of randomness; Pseudo-randomness and derandomizations;Interactive proof systems and probabilistically checkable proofs.
This course continues the content covered in 18.100 Analysis I. Roughly half of the subject is devoted to the theory of the Lebesgue integral with applications to probability, and the other half to Fourier series and Fourier integrals.
This is an advanced undergraduate course dealing with calculus in one complex variable with geometric emphasis. Since the course Analysis I (18.100B) is a prerequisite, topological notions like compactness, connectedness, and related properties of continuous functions are taken for granted.
This course offers biweekly problem sets with solutions, two term tests and a final exam, all with solutions.
This course covers harmonic theory on complex manifolds, the Hodge decomposition theorem, the Hard Lefschetz theorem, and Vanishing theorems. Some results and tools on deformation and uniformization of complex manifolds are also discussed.
This calculus course covers differentiation and integration of functions of one variable, and concludes with a brief discussion of infinite series. Calculus is fundamental to many scientific disciplines including physics, engineering, and economics.
Course Format
 This course has been designed for independent study. It includes all of the materials you will need to understand the concepts covered in this subject. The materials in this course include:
This course has been designed for independent study. It includes all of the materials you will need to understand the concepts covered in this subject. The materials in this course include:
- Lecture Videos with supporting written notes
- Recitation Videos of problem-solving tips
- Worked Examples with detailed solutions to sample problems
- Problem sets with solutions
- Exams with solutions
- Interactive Java Applets ("Mathlets") to reinforce key concepts
Content Development
David Jerison
Arthur Mattuck
Haynes Miller
Benjamin Brubaker
Jeremy Orloff
This course covers differential, integral and vector calculus for functions of more than one variable. These mathematical tools and methods are used extensively in the physical sciences, engineering, economics and computer graphics.
Course Formats
 The materials have been organized to support independent study. The website includes all of the materials you will need to understand the concepts covered in this subject. The materials in this course include:
The materials have been organized to support independent study. The website includes all of the materials you will need to understand the concepts covered in this subject. The materials in this course include:
- Lecture Videos recorded on the MIT campus
- Recitation Videos with problem-solving tips
- Examples of solutions to sample problems
- Problem for you to solve, with solutions
- Exams with solutions
- Interactive Java Applets ("Mathlets") to reinforce key concepts
Content Development
Denis Auroux
Arthur Mattuck
Jeremy Orloff
John Lewis
This course covers vector and multi-variable calculus. It is the second semester in the freshman calculus sequence. Topics include vectors and matrices, partial derivatives, double and triple integrals, and vector calculus in 2 and 3-space.
MIT OpenCourseWare offers another version of 18.02, from the Spring 2006 term. Both versions cover the same material, although they are taught by different faculty and rely on different textbooks. Multivariable Calculus (18.02) is taught during the Fall and Spring terms at MIT, and is a required subject for all MIT undergraduates.
This course provides an elementary introduction to probability and statistics with applications. Topics include: basic combinatorics, random variables, probability distributions, Bayesian inference, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and linear regression.
The Spring 2014 version of this subject employed the residential MITx system, which enables on-campus subjects to provide MIT students with learning and assessment tools such as online problem sets, lecture videos, reading questions, pre-lecture questions, problem set assistance, tutorial videos, exam review content, and even online exams.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.