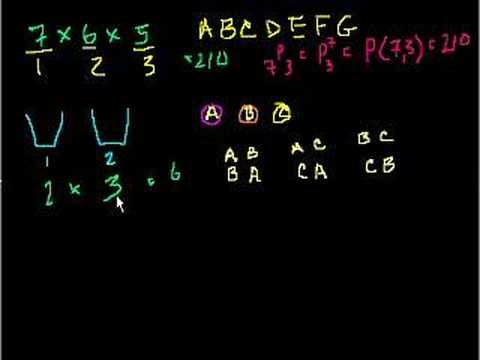Online courses directory (210)
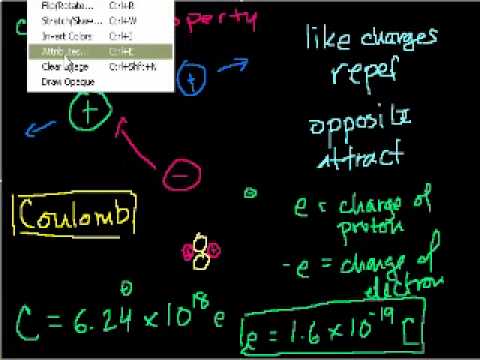
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation. Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation.
This tutorial is the meat of much of classical physics. We think about what a force is and how Newton changed the world's (and possibly your) view of how reality works. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face.
Relationship between angular velocity and speed. Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line. Introduction to Vectors and Scalars. Calculating Average Velocity or Speed. Solving for Time. Displacement from Time and Velocity Example. Acceleration. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Airbus A380 Take-off Time. Airbus A380 Take-off Distance. Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration. Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity. Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity. Projectile Height Given Time. Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time. Impact Velocity From Given Height. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2). Introduction to work and energy. Work and Energy (part 2). Conservation of Energy. Work/Energy problem with Friction. Introduction to mechanical advantage. Mechanical Advantage (part 2). Mechanical Advantage (part 3). Center of Mass. Introduction to Torque. Moments. Moments (part 2). Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Projectile motion (part 1). Projectile motion (part 2). Projectile motion (part 3). Projectile motion (part 4). Projectile motion (part 5). Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Conservation of angular momentum. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2). Viewing g as the value of Earth's Gravitational Field Near the Surface. Intro to springs and Hooke's Law. Potential energy stored in a spring. Spring potential energy example (mistake in math). Introduction to Harmonic Motion. Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus). Harmonic Motion Part 3 (no calculus).
The foundations of Pre-Algebra from The Khan Academy.
This free online course in Pre-Algebra mathematics for high school students will guide you through several different areas of mathematics such as integers, one-step equations, inequalities and equations, graphs and functions, percent, probabilities. There is also an introduction into geometry and right triangles. The course is divided into twelve modules and each module is divided into several lessons. Under each lesson you will find theory, examples and video lessons. This course is ideal for learners who want to gain a comprehensive knowledge and understanding of topics in pre-algebra which they can build on in later courses.
Non-trigonometry pre-calculus topics. Solid understanding of all of the topics in the "Algebra" playlist should make this playlist pretty digestible. Introduction to Limits (HD). Introduction to Limits. Limit Examples (part 1). Limit Examples (part 2). Limit Examples (part3). Limit Examples w/ brain malfunction on first prob (part 4). Squeeze Theorem. Proof: lim (sin x)/x. More Limits. Sequences and Series (part 1). Sequences and series (part 2). Permutations. Combinations. Binomial Theorem (part 1). Binomial Theorem (part 2). Binomial Theorem (part 3). Introduction to interest. Interest (part 2). Introduction to compound interest and e. Compound Interest and e (part 2). Compound Interest and e (part 3). Compound Interest and e (part 4). Exponential Growth. Polar Coordinates 1. Polar Coordinates 2. Polar Coordinates 3. Parametric Equations 1. Parametric Equations 2. Parametric Equations 3. Parametric Equations 4. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Basic Complex Analysis. Exponential form to find complex roots. Complex Conjugates. Series Sum Example. Complex Determinant Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Logarithmic Scale. Vi and Sal Explore How We Think About Scale. Vi and Sal Talk About the Mysteries of Benford's Law. Benford's Law Explanation (Sequel to Mysteries of Benford's Law).
Students often encounter grave difficulty in calculus if their algebraic knowledge is insufficient. This course is designed to provide students with algebraic knowledge needed for success in a typical calculus course. We explore a suite of functions used in calculus, including polynomials (with special emphasis on linear and quadratic functions), rational functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions. Along the way, basic strategies for solving equations and inequalities are reinforced, as are strategies for interpreting and manipulating a variety of algebraic expressions. Students enrolling in the course are expected to have good number sense and to have taken an intermediate algebra course.
Basic probability. Should have a reasonable grounding in basic algebra before watching. Basic Probability. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Monty Hall Problem. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Permutations. Combinations. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Conditional Probability and Combinations. Birthday Probability Problem. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Law of Large Numbers. Introduction to Random Variables. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8).
This course introduces students to the basic concepts and logic of statistical reasoning and gives the students introductory-level practical ability to choose, generate, and properly interpret appropriate descriptive and inferential methods. In addition, the course helps students gain an appreciation for the diverse applications of statistics and its relevance to their lives and fields of study. The course does not assume any prior knowledge in statistics and its only prerequisite is basic algebra. We offer two versions of statistics, each with a different emphasis: Probability and Statistics and Statistical Reasoning. Each course includes all expository text, simulations, case studies, comprehension tests, interactive learning exercises, and the StatTutor labs. Each course contains all of the instructions for the four statistics packages options we support. To do the activities, you will need your own copy of Microsoft Excel, Minitab, the open source R software, TI calculator, or StatCrunch. One of the main differences between the courses is the path through probability. Probability and Statistics includes the classical treatment of probability as it is in the earlier versions of the OLI Statistics course.
This free online course introduces you to the mathematics of probability, chance and the analysis of data. The course begins by introducing data collection and analysis, graphs and frequency distribution. The course examines chance in the context of gambling, odds and probability. The course is of interest to anybody who needs to analyse mathematical data and is particularly valuable to students studying for exams.
Measures of central tendency and dispersion. Mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance.
Introduction to probability. Independent and dependent events. Compound events. Mutual exclusive events. Addition rule for probability. Basic Probability. Probability space exercise example. Probability space. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Probability 1. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Independent probability. Frequency Stability. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Dependent probability. Monty Hall Problem. Intersection and union of sets. Relative complement or difference between sets. Universal set and absolute complement. Subset, strict subset, and superset. Bringing the set operations together. Basic set notation. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8). Introduction to Random Variables. Basic Probability. Probability space exercise example. Probability space. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Probability 1. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Independent probability. Frequency Stability. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Dependent probability. Monty Hall Problem. Intersection and union of sets. Relative complement or difference between sets. Universal set and absolute complement. Subset, strict subset, and superset. Bringing the set operations together. Basic set notation. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8). Introduction to Random Variables.
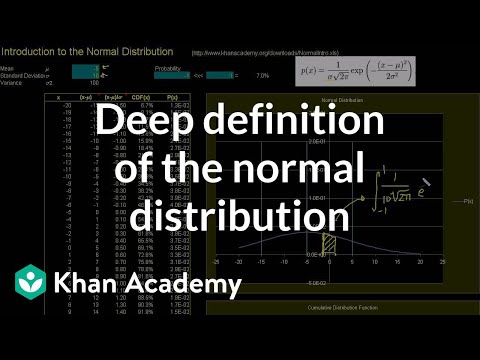
Making inferences based on sample data. Confidence intervals. Margin of error. Hypothesis testing. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic.
Permutations and combinations. Using combinatorics to solve questions in probability. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations.
Random variables. Expected value. Probability distributions (both discrete and continuous). Binomial distribution. Poisson processes. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Expected value. Law of Large Numbers. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Galton Board Exploration. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Expected value. Law of Large Numbers. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Galton Board Exploration. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2.
Fitting a line to points. Linear regression. R-squared. Correlation and Causality. Fitting a Line to Data. Estimating the line of best fit exercise. Estimating the line of best fit. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line. Correlation and Causality. Fitting a Line to Data. Estimating the line of best fit exercise. Estimating the line of best fit. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line.
“Why is math important? Why do I have to learn math?” These are typical questions that you have most likely asked at one time or another in your education. While you may learn things in math class that you will not use again, the study of mathematics is still an important one for human development. Math is widely-used in daily activities (e.g. shopping, cooking, etc.) and in most careers (e.g. medicine, teaching, engineering, construction, business, statistics in psychology, etc.). Math is also considered a “universal language.” One of the fundamental reasons why you learn math is to help you tackle problems, both mathematical and non-mathematical, with clear, concise, and logical steps. In this course, you will study important fundamental math concepts. This course begins your journey into the “Real World Math” series. These courses are intended not just to help you learn basic algebra and geometry topics, but also to show you how these topics are used in everyday life. In thi…
This introductory mathematics course is for you if you have a solid foundation in arithmetic (that is, you know how to perform operations with real numbers, including negative numbers, fractions, and decimals). Numbers and basic arithmetic are used often in everyday life in both simple situations, like estimating how much change you will get when making a purchase in a store, as well as in more complicated ones, like figuring out how much time it would take to pay off a loan under interest. The subject of algebra focuses on generalizing these procedures. For example, algebra will enable you to describe how to calculate change without specifying how much money is to be spent on a purchase-it will teach you the basic formulas and steps you need to take no matter what the specific details of the situation are. Likewise, accountants use algebraic formulas to calculate the monthly loan payments for a loan of any size under any interest rate. In this course, you will learn how to work with formulas that a…
“Everything is numbers.” This phrase was uttered by the lead character, Dr. Charlie Epps, on the hit television show “NUMB3RS.” If everything has a mathematical underpinning, then it follows that everything is somehow mathematically connected, even if it is only in some odd, “six degrees of separation (or Kevin Bacon)” kind of way. Geometry is the study of space (for now, mainly two-dimensional, with some three-dimensional thrown in) and the relationships of objects contained inside. It is one of the more relatable math courses, because it often answers that age-old question, “When am I ever going to use this in real life?” Look around you right now. Do you see any triangles? Can you spot any circles? Do you see any books that look like they are twice the size of other books? Does your wall have paint on it? In geometry, you will explore the objects that make up our universe. Most people never give a second thought to how things are constructed, but there are geometric ru…
This free online course is the second of our Upper-Secondary Mathematics suite of courses. It covers ratio and proportion, geometric sequences, arithmetic series, difference equations, linear programming, geometry, trigonometry, and graphs. This course is suitable for all math students revising for exams. It is also suitable for anyone with an interest in Mathematics. <br />
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.