Courses tagged with "Diencephalon" (38)
Organic chemistry course surveying introductory topics in structure and reactivity with an emphasis on elementary reaction mechanisms.
Organic chemistry course covering intermediate topics in structure and reactivity with special applications to the life sciences.
Elements and Atoms. Introduction to the atom. Elements and Atoms. Introduction to the atom.
Orbitals. More on orbitals and electron configuration. Electron configurations. Electron configurations 2. Valence Electrons. Orbitals. More on orbitals and electron configuration. Electron configurations. Electron configurations 2. Valence Electrons.
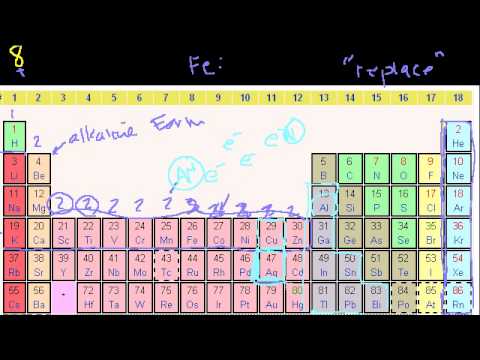
Groups of the Periodic Table. Valence Electrons. Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy. Other Periodic Table Trends. Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds. Groups of the Periodic Table. Valence Electrons. Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy. Other Periodic Table Trends. Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds.
Molecular and Empirical Formulas. The Mole and Avogadro's Number. Formula from Mass Composition. Another mass composition problem. Balancing Chemical Equations. Stoichiometry. Stoichiometry Example Problem 1. Stoichiometry Example Problem 2. Stoichiometry: Limiting Reagent. Limiting Reactant Example Problem 1. Spectrophotometry Introduction. Spectrophotometry Example. Molecular and Empirical Formulas. The Mole and Avogadro's Number. Formula from Mass Composition. Another mass composition problem. Balancing Chemical Equations. Stoichiometry. Stoichiometry Example Problem 1. Stoichiometry Example Problem 2. Stoichiometry: Limiting Reagent. Limiting Reactant Example Problem 1. Spectrophotometry Introduction. Spectrophotometry Example.
Ideal Gas Equation: PV=nRT. Ideal Gas Equation Example 1. Ideal Gas Equation Example 2. Ideal Gas Equation Example 3. Ideal Gas Equation Example 4. Partial Pressure. Vapor Pressure Example. Ideal Gas Equation: PV=nRT. Ideal Gas Equation Example 1. Ideal Gas Equation Example 2. Ideal Gas Equation Example 3. Ideal Gas Equation Example 4. Partial Pressure. Vapor Pressure Example.
States of Matter. States of Matter Follow-Up. Specific Heat, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization. Chilling Water Problem. Phase Diagrams. Van Der Waals Forces. Covalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals. Vapor Pressure. Suspensions, Colloids and Solutions. Solubility. Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Suppression. Change of State Example. States of Matter. States of Matter Follow-Up. Specific Heat, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization. Chilling Water Problem. Phase Diagrams. Van Der Waals Forces. Covalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals. Vapor Pressure. Suspensions, Colloids and Solutions. Solubility. Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Suppression. Change of State Example.
Introduction to Oxidation States. More on Oxidation States. Hydrogen Peroxide Correction. Redox Reactions. Galvanic Cells. Introduction to Oxidation States. More on Oxidation States. Hydrogen Peroxide Correction. Redox Reactions. Galvanic Cells.
Types of Decay. Half-Life. Exponential Decay Formula Proof (can skip, involves Calculus). Introduction to Exponential Decay. More Exponential Decay Examples. Types of Decay. Half-Life. Exponential Decay Formula Proof (can skip, involves Calculus). Introduction to Exponential Decay. More Exponential Decay Examples.
This course provides an introduction to the chemistry of biological, inorganic, and organic molecules. The emphasis is o
Organic Chemistry of Macromolecules covers the preparation, reactions, and properties of high molecular weight polymeric materials of both natural and synthetic origin. As a part of this course, U-M students collaboratively created and edited Wikipedia articles. Course Level: Graduate This Work, Chemistry 538 - Organic Chemistry of Macromolecules, by Anne McNeil is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license.
Introduction to Kinetics. Reactions in Equilibrium. Mini-Video on Ion Size. Keq Intuition (mathy and not necessary to progress). Keq derivation intuition (can skip; bit mathy). Heterogeneous Equilibrium. Le Chatelier's Principle. Introduction to pH, pOH, and pKw. Introduction to Kinetics. Reactions in Equilibrium. Mini-Video on Ion Size. Keq Intuition (mathy and not necessary to progress). Keq derivation intuition (can skip; bit mathy). Heterogeneous Equilibrium. Le Chatelier's Principle. Introduction to pH, pOH, and pKw.
Acid Base Introduction. pH, pOH of Strong Acids and Bases. pH of a Weak Acid. pH of a Weak Base. Conjugate Acids and Bases. pKa and pKb Relationship. Buffers and Hendersen-Hasselbalch. Strong Acid Titration. Weak Acid Titration. Half Equivalence Point. Titration Roundup. Acid Base Titration. Acid Base Introduction. pH, pOH of Strong Acids and Bases. pH of a Weak Acid. pH of a Weak Base. Conjugate Acids and Bases. pKa and pKb Relationship. Buffers and Hendersen-Hasselbalch. Strong Acid Titration. Weak Acid Titration. Half Equivalence Point. Titration Roundup. Acid Base Titration.
Get a basic overview of microbiology before exploring advanced topics like bacterial cell morphology, nitrogen fixation and protozoan diseases through this online Education Portal course, Biology 103: Microbiology. Watch our video lessons on STDs, bacterial diseases and foodborne illnesses as you prepare to earn real college credit through the Microbiology Excelsior Exam . Though the subjects covered in these lessons are somewhat intense, our experienced, knowledgeable instructors have kept the videos brief, engaging and easy to follow. You also can benefit from the multiple-choice quizzes and written transcripts that complement each video.
Physics 101 is the first course in the Introduction to Physics sequence. In general, the quest of physics is to develop descriptions of the natural world that correspond closely to actual observations. Given this definition, the story behind everything in the universe is one of physics. In practice, the field of physics is more often limited to the discovery and refinement of the basic laws that underlie the behavior of matter and energy. While biology is founded upon physics, in practice, the study of biology generally assumes that the present understanding of physical laws is accurate. Chemistry is more closely dependent on physics and assumes that physical laws provide accurate predictions. Engineering, for the most part, is applied physics. In this course, we will study physics from the ground up, learning the basic principles of physical laws, their application to the behavior of objects, and the use of the scientific method in driving advances in this knowledge. This first course o…
The physics of the Universe appears to be dominated by the effects of four fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetism, and weak and strong nuclear forces. These control how matter, energy, space, and time interact to produce our physical world. All other forces, such as the force you exert in standing up, are ultimately derived from these fundamental forces. We have direct daily experience with two of these forces: gravity and electromagnetism. Consider, for example, the everyday sight of a person sitting on a chair. The force holding the person on the chair is gravitational, while that gravitational force is balanced by material forces that “push up” to keep the individual in place, and these forces are the direct result of electromagnetic forces on the nanoscale. On a larger stage, gravity holds the celestial bodies in their orbits, while we see the Universe by the electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) with which it is filled. The electromagnetic force also makes possible the a…
This course is designed to introduce you to the study of Calculus. You will learn concrete applications of how calculus is used and, more importantly, why it works. Calculus is not a new discipline; it has been around since the days of Archimedes. However, Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz, two 17th-century European mathematicians concurrently working on the same intellectual discovery hundreds of miles apart, were responsible for developing the field as we know it today. This brings us to our first question, what is today's Calculus? In its simplest terms, calculus is the study of functions, rates of change, and continuity. While you may have cultivated a basic understanding of functions in previous math courses, in this course you will come to a more advanced understanding of their complexity, learning to take a closer look at their behaviors and nuances. In this course, we will address three major topics: limits, derivatives, and integrals, as well as study their respective foundations and a…
This course is the second installment of Single-Variable Calculus. In Part I (MA101) [1], we studied limits, derivatives, and basic integrals as a means to understand the behavior of functions. In this course (Part II), we will extend our differentiation and integration abilities and apply the techniques we have learned. Additional integration techniques, in particular, are a major part of the course. In Part I, we learned how to integrate by various formulas and by reversing the chain rule through the technique of substitution. In Part II, we will learn some clever uses of substitution, how to reverse the product rule for differentiation through a technique called integration by parts, and how to rewrite trigonometric and rational integrands that look impossible into simpler forms. Series, while a major topic in their own right, also serve to extend our integration reach: they culminate in an application that lets you integrate almost any function you’d like. Integration allows us to calculat…
This chemistry survey is designed to introduce students to the world of chemistry. The principles of chemistry were first identified, studied, and applied by ancient Egyptians in order to extract metal from ores, make alcoholic beverages, glaze pottery, turn fat into soap, and much more. What began as a quest to build better weapons or create potions capable of ensuring everlasting life has since become the foundation of modern science. Take a look around you: chemistry makes up almost everything you touch, see, and feel, from the shampoo you used this morning to the plastic container that holds your lunch. In this course, we will study chemistry from the ground up, learning the basics of the atom and its behavior. We will use this knowledge to understand the chemical properties of matter and the changes and reactions that take place in all types of matter.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.