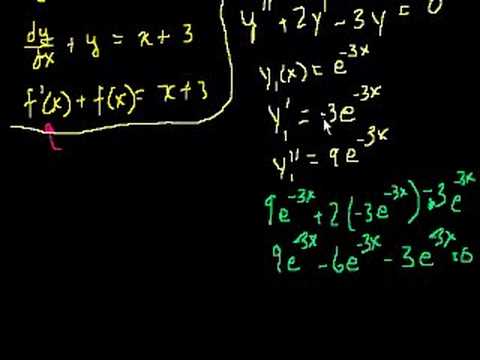Courses tagged with "Class2Go" (107)
CA Algebra I: Number Properties and Absolute Value. CA Algebra I: Simplifying Expressions. CA Algebra I: Simple Logical Arguments. CA Algebra I: Graphing Inequalities. CA Algebra I: Slope and Y-intercept. CA Algebra I: Systems of Inequalities. CA Algebra I: Simplifying Expressions. CA Algebra I: Factoring Quadratics. CA Algebra I: Completing the Square. CA Algebra I: Quadratic Equation. CA Algebra I: Quadratic Roots. CA Algebra I: Rational Expressions 1. CA Algebra I: Rational Expressions 2. CA Algebra I: Word Problems. CA Algebra I: More Word Problems. CA Algebra I: Functions.
California Standards Test: Algebra II. California Standards Test: Algebra II (Graphing Inequalities). CA Standards: Algebra II (Algebraic Division/Multiplication). CA Standards: Algebra II. Algebra II: Simplifying Polynomials. Algebra II: Imaginary and Complex Numbers. Algebra II: Complex numbers and conjugates. Algebra II: Quadratics and Shifts. Examples: Graphing and interpreting quadratics. Hyperbola and parabola examples. Algebra II: Circles and Logarithms. Algebra II: Logarithms Exponential Growth. Algebra II: Logarithms and more. Algebra II: Functions, Combinatorics. Algebra II: binomial Expansion and Combinatorics. Algebra II: Binomial Expansions, Geometric Series Sum. Algebra II: Functions and Probability. Algebra II: Probability and Statistics. Algebra II: Mean and Standard Deviation.
CA Geometry: deductive reasoning. CA Geometry: Proof by Contradiction. CA Geometry: More Proofs. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 1. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 2. CA Geometry: More on congruent and similar triangles. CA Geometry: Triangles and Parallelograms. CA Geometry: Area, Pythagorean Theorem. CA Geometry: Area, Circumference, Volume. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Area. CA Geometry: Exterior Angles. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Compass Constructions. CA Geometry: Compass Construction. CA Geometry: Basic Trigonometry. CA Geometry: More Trig. CA Geometry: Circle Area Chords Tangent. CA Geometry: Secants and Translations.
Sal does the 80 problems from the released questions from the California Standards Test for Geometry. Basic understanding of Algebra I necessary. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Challenging Perimeter Problem. CA Geometry: deductive reasoning. CA Geometry: Proof by Contradiction. CA Geometry: More Proofs. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 1. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 2. CA Geometry: More on congruent and similar triangles. CA Geometry: Triangles and Parallelograms. CA Geometry: Area, Pythagorean Theorem. CA Geometry: Area, Circumference, Volume. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Area. CA Geometry: Exterior Angles. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Compass Constructions. CA Geometry: Compass Construction. CA Geometry: Basic Trigonometry. CA Geometry: More Trig. CA Geometry: Circle Area Chords Tangent. CA Geometry: Secants and Translations. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Challenging Perimeter Problem. CA Geometry: deductive reasoning. CA Geometry: Proof by Contradiction. CA Geometry: More Proofs. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 1. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 2. CA Geometry: More on congruent and similar triangles. CA Geometry: Triangles and Parallelograms. CA Geometry: Area, Pythagorean Theorem. CA Geometry: Area, Circumference, Volume. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Area. CA Geometry: Exterior Angles. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Compass Constructions. CA Geometry: Compass Construction. CA Geometry: Basic Trigonometry. CA Geometry: More Trig. CA Geometry: Circle Area Chords Tangent. CA Geometry: Secants and Translations.
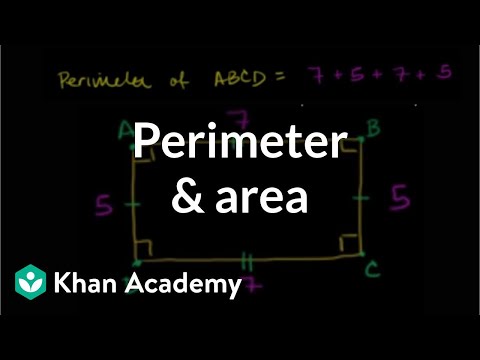
A broad set of tutorials covering perimeter area and volume with and without algebra. Perimeter and Area Basics. Area and Perimeter. Perimeter of a Polygon. Perimeter of a shape. Perimeter 1. Finding dimensions given perimeter. Area 1. Finding dimensions given area. Perimeter and Area Basics. Triangle Area Proofs. Area of triangles. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Area of Diagonal Generated Triangles of Rectangle are Equal. Area of an equilateral triangle. Area of shaded region made from equilateral triangles. Shaded areas. Challenging Perimeter Problem. Triangle inqequality theorem. Triangle inequality theorem. Koch Snowflake Fractal. Area of an equilateral triangle. Area of Koch Snowflake (part 1) - Advanced. Area of Koch Snowflake (part 2) - Advanced. Heron's Formula. Heron's formula. Part 1 of Proof of Heron's Formula. Part 2 of the Proof of Heron's Formula. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Parts of a Circle. Radius diameter and circumference. Area of a Circle. Area of a circle. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of parallelograms. Area of a trapezoid. Area of a kite. Area of trapezoids, rhombi, and kites. Perimeter of a Polygon. Perimeter and Area of a Non-Standard Polygon. How we measure volume. Measuring volume with unit cubes. Volume with unit cubes. Measuring volume as area times length. Volume of a rectangular prism or box examples. Volume 1. Volume word problem example. Volume word problems. Solid Geometry Volume. Cylinder Volume and Surface Area. Volume of a Sphere. Solid geometry. Perimeter and Area Basics. Area and Perimeter. Perimeter of a Polygon. Perimeter of a shape. Perimeter 1. Finding dimensions given perimeter. Area 1. Finding dimensions given area. Perimeter and Area Basics. Triangle Area Proofs. Area of triangles. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Area of Diagonal Generated Triangles of Rectangle are Equal. Area of an equilateral triangle. Area of shaded region made from equilateral triangles. Shaded areas. Challenging Perimeter Problem. Triangle inqequality theorem. Triangle inequality theorem. Koch Snowflake Fractal. Area of an equilateral triangle. Area of Koch Snowflake (part 1) - Advanced. Area of Koch Snowflake (part 2) - Advanced. Heron's Formula. Heron's formula. Part 1 of Proof of Heron's Formula. Part 2 of the Proof of Heron's Formula. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Parts of a Circle. Radius diameter and circumference. Area of a Circle. Area of a circle. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of parallelograms. Area of a trapezoid. Area of a kite. Area of trapezoids, rhombi, and kites. Perimeter of a Polygon. Perimeter and Area of a Non-Standard Polygon. How we measure volume. Measuring volume with unit cubes. Volume with unit cubes. Measuring volume as area times length. Volume of a rectangular prism or box examples. Volume 1. Volume word problem example. Volume word problems. Solid Geometry Volume. Cylinder Volume and Surface Area. Volume of a Sphere. Solid geometry.
Non-trigonometry pre-calculus topics. Solid understanding of all of the topics in the "Algebra" playlist should make this playlist pretty digestible. Introduction to Limits (HD). Introduction to Limits. Limit Examples (part 1). Limit Examples (part 2). Limit Examples (part3). Limit Examples w/ brain malfunction on first prob (part 4). Squeeze Theorem. Proof: lim (sin x)/x. More Limits. Sequences and Series (part 1). Sequences and series (part 2). Permutations. Combinations. Binomial Theorem (part 1). Binomial Theorem (part 2). Binomial Theorem (part 3). Introduction to interest. Interest (part 2). Introduction to compound interest and e. Compound Interest and e (part 2). Compound Interest and e (part 3). Compound Interest and e (part 4). Exponential Growth. Polar Coordinates 1. Polar Coordinates 2. Polar Coordinates 3. Parametric Equations 1. Parametric Equations 2. Parametric Equations 3. Parametric Equations 4. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Basic Complex Analysis. Exponential form to find complex roots. Complex Conjugates. Series Sum Example. Complex Determinant Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Logarithmic Scale. Vi and Sal Explore How We Think About Scale. Vi and Sal Talk About the Mysteries of Benford's Law. Benford's Law Explanation (Sequel to Mysteries of Benford's Law).
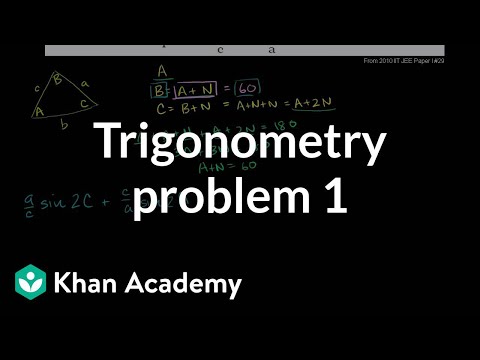
Questions from previous IIT JEEs. IIT JEE Trigonometry Problem 1. IIT JEE Perpendicular Planes (Part 1). IIT JEE Perpendicular Plane (part 2). IIT JEE Complex Root Probability (part 1). IIT JEE Complex Root Probability (part 2). IIT JEE Position Vectors. IIT JEE Integral Limit. IIT JEE Algebraic Manipulation. IIT JEE Function Maxima. IIT JEE Diameter Slope. IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (part 1). IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (Part 2). IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (Part 3). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 1). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 2). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 3). IIT JEE Differentiability and Boundedness. IIT JEE Integral with Binomial Expansion. IIT JEE Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices. IIT JEE Trace and Determinant. IIT JEE Divisible Determinants. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Intersection. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 1. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 2. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 3. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 4. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 5. IIT JEE Trigonometric Constraints. IIT JEE Trigonometric Maximum. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). IIT JEE Lagrange's Formula. Tangent Line Hyperbola Relationship (very optional). 2010 IIT JEE Paper 1 Problem 50 Hyperbola Eccentricity. Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Complex Determinant Example. Series Sum Example. Trigonometric System Example. Simple Differential Equation Example. IIT JEE Trigonometry Problem 1. IIT JEE Perpendicular Planes (Part 1). IIT JEE Perpendicular Plane (part 2). IIT JEE Complex Root Probability (part 1). IIT JEE Complex Root Probability (part 2). IIT JEE Position Vectors. IIT JEE Integral Limit. IIT JEE Algebraic Manipulation. IIT JEE Function Maxima. IIT JEE Diameter Slope. IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (part 1). IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (Part 2). IIT JEE Hairy Trig and Algebra (Part 3). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 1). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 2). IIT JEE Complex Numbers (part 3). IIT JEE Differentiability and Boundedness. IIT JEE Integral with Binomial Expansion. IIT JEE Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices. IIT JEE Trace and Determinant. IIT JEE Divisible Determinants. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Intersection. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 1. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 2. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 3. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 4. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 5. IIT JEE Trigonometric Constraints. IIT JEE Trigonometric Maximum. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). IIT JEE Lagrange's Formula. Tangent Line Hyperbola Relationship (very optional). 2010 IIT JEE Paper 1 Problem 50 Hyperbola Eccentricity. Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Complex Determinant Example. Series Sum Example. Trigonometric System Example. Simple Differential Equation Example.
Basic probability. Should have a reasonable grounding in basic algebra before watching. Basic Probability. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Monty Hall Problem. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Permutations. Combinations. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Conditional Probability and Combinations. Birthday Probability Problem. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Law of Large Numbers. Introduction to Random Variables. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8).
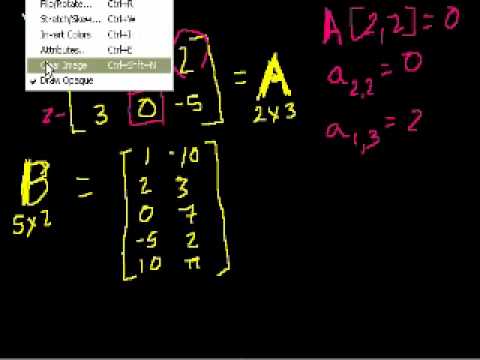
Matrices, vectors, vector spaces, transformations. Covers all topics in a first year college linear algebra course. This is an advanced course normally taken by science or engineering majors after taking at least two semesters of calculus (although calculus really isn't a prereq) so don't confuse this with regular high school algebra. Introduction to matrices. Matrix multiplication (part 1). Matrix multiplication (part 2). Idea Behind Inverting a 2x2 Matrix. Inverting matrices (part 2). Inverting Matrices (part 3). Matrices to solve a system of equations. Matrices to solve a vector combination problem. Singular Matrices. 3-variable linear equations (part 1). Solving 3 Equations with 3 Unknowns. Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A). A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Orthogonal Complements. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes.
Identifying types of quadrilaterals, finding measurements, and applying and proving postulates. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of a Regular Hexagon. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Rhombus Diagonals. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of a Regular Hexagon. Problem involving angle derived from square and circle. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures.
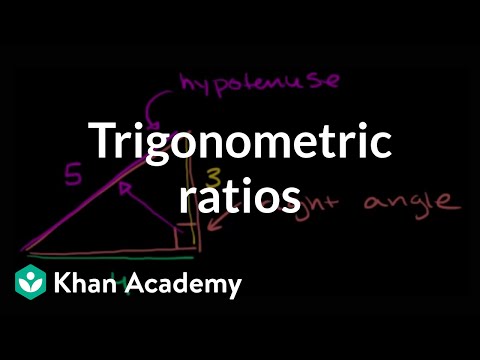
Videos on trigonometry. Watch the "Geometry" playlist first if you have trouble understanding the topics covered here. Basic Trigonometry. Basic Trigonometry II. Radians and degrees. Using Trig Functions. Using Trig Functions Part II. The unit circle definition of trigonometric function. Unit Circle Definition of Trig Functions. Graph of the sine function. Graphs of trig functions. Graphing trig functions. More trig graphs. Determining the equation of a trigonometric function. Trigonometric Identities. Proof: sin(a+b) = (cos a)(sin b) + (sin a)(cos b). Proof: cos(a+b) = (cos a)(cos b)-(sin a)(sin b). Trig identities part 2 (parr 4 if you watch the proofs). Trig identies part 3 (part 5 if you watch the proofs). Trigonometry word problems (part 1). Trigonometry word problems (part 2). Law of cosines. Navigation Word Problem. Proof: Law of Sines. Ferris Wheel Trig Problem. Ferris Wheel Trig Problem (part 2). Fun Trig Problem. Polar Coordinates 1. Polar Coordinates 2. Polar Coordinates 3. Inverse Trig Functions: Arcsin. Inverse Trig Functions: Arctan. Inverse Trig Functions: Arccos. Trigonometry Identity Review/Fun. Tau versus Pi. IIT JEE Trigonometry Problem 1. IIT JEE Trigonometric Maximum. IIT JEE Trigonometric Constraints. Trigonometric System Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 11.avi. 2003 AIME II Problem 14.
Topics covered in a first year course in differential equations. Need to understand basic differentiation and integration from Calculus playlist before starting here. What is a differential equation. Separable Differential Equations. Separable differential equations 2. Exact Equations Intuition 1 (proofy). Exact Equations Intuition 2 (proofy). Exact Equations Example 1. Exact Equations Example 2. Exact Equations Example 3. Integrating factors 1. Integrating factors 2. First order homegenous equations. First order homogeneous equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4. Laplace Transform 1. Laplace Transform 2. Laplace Transform 3 (L{sin(at)}). Laplace Transform 4. Laplace Transform 5. Laplace Transform 6. Laplace Transform to solve an equation. Laplace Transform solves an equation 2. More Laplace Transform tools. Using the Laplace Transform to solve a nonhomogeneous eq. Laplace Transform of : L{t}. Laplace Transform of t^n: L{t^n}. Laplace Transform of the Unit Step Function. Inverse Laplace Examples. Laplace/Step Function Differential Equation. Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform of the Dirac Delta Function. Introduction to the Convolution. The Convolution and the Laplace Transform. Using the Convolution Theorem to Solve an Initial Value Prob.
Topics covered in a traditional college level introductory microeconomics course. Production Possibilities Frontier. Opportunity Cost. Increasing Opportunity Cost. Allocative Efficiency and Marginal Benefit. Economic Growth through Investment. Comparative Advantage Specialization and Gains from Trade. Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage. Law of Demand. Price of Related Products and Demand. Changes in Income, Population, or Preferences. Normal and Inferior Goods. Inferior Goods Clarification. Law of Supply. Factors Affecting Supply. Market Equilibrium. Changes in Market Equilibrium. Price Elasticity of Demand. More on Elasticity of Demand. Perfect Inelasticity and Perfect Elasticity of Demand. Constant Unit Elasticity. Total Revenue and Elasticity. More on Total Revenue and Elasticity. Cross Elasticity of Demand. Elasticity of Supply. Elasticity and Strange Percent Changes. Demand Curve as Marginal Benefit Curve. Consumer Surplus Introduction. Total Consumer Surplus as Area. Producer Surplus. Rent Control and Deadweight Loss. Minimum Wage and Price Floors. Taxation and Dead Weight Loss. Percentage Tax on Hamburgers. Taxes and Perfectly Inelastic Demand. Taxes and Perfectly Elastic Demand. Marginal Utility. Equalizing Marginal Utility per Dollar Spent. Deriving Demand Curve from Tweaking Marginal Utility per Dollar. Budget Line. Optimal Point on Budget Line. Types of Indifference Curves. Economic Profit vs Accounting Profit. Depreciation and Opportunity Cost of Capital. Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost.. Visualizing Average Costs and Marginal Costs as Slope. Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. Marginal Revenue Below Average Total Cost. Long Term Supply Curve and Economic Profit. Perfect Competition. Monopoly Basics. Review of Revenue and Cost Graphs for a Monopoly. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 1)- Total Revenue.. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 2)- Marginal Revenue. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 3)- Dead Weight Loss.avi. Optional Calculus Proof to Show that MR has Twice Slope of Demand. Oligopolies and Monopolistic Competition. Monopolistic Competition and Economic Profit. Oligopolies, Duopolies, Collusion, and Cartels. Prisoners' Dilemma and Nash Equilibrium. More on Nash Equilibrium. Why Parties to Cartels Cheat. Game Theory of Cheating Firms. Negative Externalities. Taxes for Factoring in Negative Externalities. Positive Externalities. Tragedy of the Commons. First Degree Price Discrimination. A Firm's Marginal Product Revenue Curve. How Many People to Hire Given the MPR curve. Adding Demand Curves.
Calculating derivatives. Power rule. Product and quotient rules. Chain Rule. Implicit differentiation. Derivatives of common functions. Newton Leibniz and Usain Bolt. Slope of a line secant to a curve. Slope of a secant line example 1. Slope of a secant line example 2. Slope of a secant line example 3. Approximating instantaneous rate of change word problem. Approximating equation of tangent line word problem. Slope of secant lines. Derivative as slope of a tangent line. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 1. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 2. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 3. Tangent slope is limiting value of secant slope. Calculating slope of tangent line using derivative definition. Derivatives 1. The derivative of f(x)=x^2 for any x. Formal and alternate form of the derivative. Formal and alternate form of the derivative for ln x. Formal and alternate form of the derivative example 1. The formal and alternate form of the derivative. Interpreting slope of a curve exercise. Recognizing slope of curves. Calculus: Derivatives 1. Calculus: Derivatives 2. Derivative Intuition Module. Derivative intuition. Graphs of functions and their derivatives example 1. Where a function is not differentiable. Identifying a function's derivative example. Figuring out which function is the the derivative. Graphs of functions and their derivatives. Intuitively drawing the derivative of a function. Intuitively drawing the antiderivative of a function. Visualizing derivatives exercise. Visualizing derivatives. Power Rule. Is the power rule reasonable. Derivative properties and polynomial derivatives. Power rule. Proof: d/dx(x^n). Proof: d/dx(sqrt(x)). Power rule introduction. Derivatives of sin x, cos x, tan x, e^x and ln x. Special derivatives. Chain rule introduction. Chain rule definition and example. Chain rule with triple composition. Chain rule for derivative of 2^x. Derivative of log with arbitrary base. Chain rule 1. Extreme Derivative Word Problem (advanced). The Chain Rule. Chain Rule Examples. Even More Chain Rule. More examples using multiple rules. Derivatives of sin x, cos x, tan x, e^x and ln x. Special derivatives. Applying the product rule for derivatives. Product rule for more than two functions. Product rule. Quotient rule from product rule. Quotient rule for derivative of tan x. Quotient rule. Using the product rule and the chain rule. Product Rule. Quotient rule and common derivatives. Equation of a tangent line. Implicit differentiation. Showing explicit and implicit differentiation give same result. Implicit derivative of (x-y)^2 = x + y + 1. Implicit derivative of y = cos(5x - 3y). Implicit derivative of (x^2+y^2)^3 = 5x^2y^2. Finding slope of tangent line with implicit differentiation. Implicit derivative of e^(xy^2) = x - y. Derivative of x^(x^x). Implicit differentiation. Proof: d/dx(ln x) = 1/x. Proof: d/dx(e^x) = e^x. Proofs of derivatives of ln(x) and e^x. Newton Leibniz and Usain Bolt. Slope of a line secant to a curve. Slope of a secant line example 1. Slope of a secant line example 2. Slope of a secant line example 3. Approximating instantaneous rate of change word problem. Approximating equation of tangent line word problem. Slope of secant lines. Derivative as slope of a tangent line. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 1. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 2. Tangent slope as limiting value of secant slope example 3. Tangent slope is limiting value of secant slope. Calculating slope of tangent line using derivative definition. Derivatives 1. The derivative of f(x)=x^2 for any x. Formal and alternate form of the derivative. Formal and alternate form of the derivative for ln x. Formal and alternate form of the derivative example 1. The formal and alternate form of the derivative. Interpreting slope of a curve exercise. Recognizing slope of curves. Calculus: Derivatives 1. Calculus: Derivatives 2. Derivative Intuition Module. Derivative intuition. Graphs of functions and their derivatives example 1. Where a function is not differentiable. Identifying a function's derivative example. Figuring out which function is the the derivative. Graphs of functions and their derivatives. Intuitively drawing the derivative of a function. Intuitively drawing the antiderivative of a function. Visualizing derivatives exercise. Visualizing derivatives. Power Rule. Is the power rule reasonable. Derivative properties and polynomial derivatives. Power rule. Proof: d/dx(x^n). Proof: d/dx(sqrt(x)). Power rule introduction. Derivatives of sin x, cos x, tan x, e^x and ln x. Special derivatives. Chain rule introduction. Chain rule definition and example. Chain rule with triple composition. Chain rule for derivative of 2^x. Derivative of log with arbitrary base. Chain rule 1. Extreme Derivative Word Problem (advanced). The Chain Rule. Chain Rule Examples. Even More Chain Rule. More examples using multiple rules. Derivatives of sin x, cos x, tan x, e^x and ln x. Special derivatives. Applying the product rule for derivatives. Product rule for more than two functions. Product rule. Quotient rule from product rule. Quotient rule for derivative of tan x. Quotient rule. Using the product rule and the chain rule. Product Rule. Quotient rule and common derivatives. Equation of a tangent line. Implicit differentiation. Showing explicit and implicit differentiation give same result. Implicit derivative of (x-y)^2 = x + y + 1. Implicit derivative of y = cos(5x - 3y). Implicit derivative of (x^2+y^2)^3 = 5x^2y^2. Finding slope of tangent line with implicit differentiation. Implicit derivative of e^(xy^2) = x - y. Derivative of x^(x^x). Implicit differentiation. Proof: d/dx(ln x) = 1/x. Proof: d/dx(e^x) = e^x. Proofs of derivatives of ln(x) and e^x.
Indefinite integral as anti-derivative. Definite integral as area under a curve. Integration by parts. U-substitution. Trig substitution. Antiderivatives and indefinite integrals. Indefinite integrals of x raised to a power. Antiderivative of hairier expression. Basic trig and exponential antiderivatives. Antiderivative of x^-1. Simple Riemann approximation using rectangles. Generalizing a left Riemann sum with equally spaced rectangles. Rectangular and trapezoidal Riemann approximations. Trapezoidal approximation of area under curve. Riemann sums and integrals. Deriving integration by parts formula. Antiderivative of xcosx using integration by parts. Integral of ln x. Integration by parts twice for antiderivative of (x^2)(e^x). Integration by parts of (e^x)(cos x). U-substitution. U-substitution example 2. U-substitution Example 3. U-substitution with ln(x). Doing u-substitution twice (second time with w). U-substitution and back substitution. U-substitution with definite integral. (2^ln x)/x Antiderivative Example. Another u-substitution example. Riemann sums and integrals. Intuition for Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Evaluating simple definite integral. Definite integrals and negative area. Area between curves. Area between curves with multiple boundaries. Challenging definite integration. Introduction to definite integrals. Definite integrals (part II). Definite Integrals (area under a curve) (part III). Definite Integrals (part 4). Definite Integrals (part 5). Definite integral with substitution. Introduction to trig substitution. Another substitution with x=sin (theta). Integrals: Trig Substitution 1. Trig and U substitution together (part 1). Trig and U substitution together (part 2). Trig substitution with tangent. Integrals: Trig Substitution 2. Integrals: Trig Substitution 3 (long problem). Fundamental theorem of calculus. Applying the fundamental theorem of calculus. Swapping the bounds for definite integral. Both bounds being a function of x. Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Connecting the first and second fundamental theorems of calculus. Introduction to improper integrals. Improper integral with two infinite bounds. Divergent improper integral. Antiderivatives and indefinite integrals. Indefinite integrals of x raised to a power. Antiderivative of hairier expression. Basic trig and exponential antiderivatives. Antiderivative of x^-1. Simple Riemann approximation using rectangles. Generalizing a left Riemann sum with equally spaced rectangles. Rectangular and trapezoidal Riemann approximations. Trapezoidal approximation of area under curve. Riemann sums and integrals. Deriving integration by parts formula. Antiderivative of xcosx using integration by parts. Integral of ln x. Integration by parts twice for antiderivative of (x^2)(e^x). Integration by parts of (e^x)(cos x). U-substitution. U-substitution example 2. U-substitution Example 3. U-substitution with ln(x). Doing u-substitution twice (second time with w). U-substitution and back substitution. U-substitution with definite integral. (2^ln x)/x Antiderivative Example. Another u-substitution example. Riemann sums and integrals. Intuition for Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Evaluating simple definite integral. Definite integrals and negative area. Area between curves. Area between curves with multiple boundaries. Challenging definite integration. Introduction to definite integrals. Definite integrals (part II). Definite Integrals (area under a curve) (part III). Definite Integrals (part 4). Definite Integrals (part 5). Definite integral with substitution. Introduction to trig substitution. Another substitution with x=sin (theta). Integrals: Trig Substitution 1. Trig and U substitution together (part 1). Trig and U substitution together (part 2). Trig substitution with tangent. Integrals: Trig Substitution 2. Integrals: Trig Substitution 3 (long problem). Fundamental theorem of calculus. Applying the fundamental theorem of calculus. Swapping the bounds for definite integral. Both bounds being a function of x. Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Connecting the first and second fundamental theorems of calculus. Introduction to improper integrals. Improper integral with two infinite bounds. Divergent improper integral.
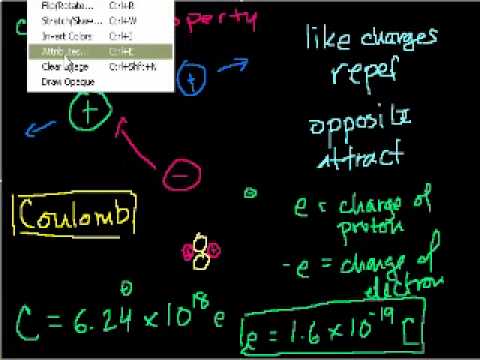
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation. Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation.
Parameterizing a surface. Surface integrals. Stokes' theorem. Introduction to Parametrizing a Surface with Two Parameters. Determining a Position Vector-Valued Function for a Parametrization of Two Parameters. Partial Derivatives of Vector-Valued Functions. Introduction to the Surface Integral. Example of calculating a surface integral part 1. Example of calculating a surface integral part 2. Example of calculating a surface integral part 3. Surface Integral Example Part 1 - Parameterizing the Unit Sphere. Surface Integral Example Part 2 - Calculating the Surface Differential. Surface Integral Example Part 3 - The Home Stretch. Surface Integral Ex2 part 1 - Parameterizing the Surface. Surface Integral Ex2 part 2 - Evaluating Integral. Surface Integral Ex3 part 1 - Parameterizing the Outside Surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 2 - Evaluating the Outside Surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 3 - Top surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 4 - Home Stretch. Conceptual Understanding of Flux in Three Dimensions. Constructing a unit normal vector to a surface. Vector representation of a Surface Integral. Stokes' Theorem Intuition. Green's and Stokes' Theorem Relationship. Orienting Boundary with Surface. Orientation and Stokes. Conditions for Stokes Theorem. Stokes Example Part 1. Part 2 Parameterizing the Surface. Stokes Example Part 3 - Surface to Double Integral. Stokes Example Part 4 - Curl and Final Answer. Evaluating Line Integral Directly - Part 1. Evaluating Line Integral Directly - Part 2. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 1. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 2. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 3. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 4. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 5. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 6. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 7. Introduction to Parametrizing a Surface with Two Parameters. Determining a Position Vector-Valued Function for a Parametrization of Two Parameters. Partial Derivatives of Vector-Valued Functions. Introduction to the Surface Integral. Example of calculating a surface integral part 1. Example of calculating a surface integral part 2. Example of calculating a surface integral part 3. Surface Integral Example Part 1 - Parameterizing the Unit Sphere. Surface Integral Example Part 2 - Calculating the Surface Differential. Surface Integral Example Part 3 - The Home Stretch. Surface Integral Ex2 part 1 - Parameterizing the Surface. Surface Integral Ex2 part 2 - Evaluating Integral. Surface Integral Ex3 part 1 - Parameterizing the Outside Surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 2 - Evaluating the Outside Surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 3 - Top surface. Surface Integral Ex3 part 4 - Home Stretch. Conceptual Understanding of Flux in Three Dimensions. Constructing a unit normal vector to a surface. Vector representation of a Surface Integral. Stokes' Theorem Intuition. Green's and Stokes' Theorem Relationship. Orienting Boundary with Surface. Orientation and Stokes. Conditions for Stokes Theorem. Stokes Example Part 1. Part 2 Parameterizing the Surface. Stokes Example Part 3 - Surface to Double Integral. Stokes Example Part 4 - Curl and Final Answer. Evaluating Line Integral Directly - Part 1. Evaluating Line Integral Directly - Part 2. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 1. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 2. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 3. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 4. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 5. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 6. Stokes' Theorem Proof Part 7.
Exploring a world where both sides aren't equal anymore!. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1.
Relationship between angular velocity and speed. Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line. Introduction to Vectors and Scalars. Calculating Average Velocity or Speed. Solving for Time. Displacement from Time and Velocity Example. Acceleration. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Airbus A380 Take-off Time. Airbus A380 Take-off Distance. Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration. Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity. Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity. Projectile Height Given Time. Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time. Impact Velocity From Given Height. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2). Introduction to work and energy. Work and Energy (part 2). Conservation of Energy. Work/Energy problem with Friction. Introduction to mechanical advantage. Mechanical Advantage (part 2). Mechanical Advantage (part 3). Center of Mass. Introduction to Torque. Moments. Moments (part 2). Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Projectile motion (part 1). Projectile motion (part 2). Projectile motion (part 3). Projectile motion (part 4). Projectile motion (part 5). Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Conservation of angular momentum. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2). Viewing g as the value of Earth's Gravitational Field Near the Surface. Intro to springs and Hooke's Law. Potential energy stored in a spring. Spring potential energy example (mistake in math). Introduction to Harmonic Motion. Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus). Harmonic Motion Part 3 (no calculus).
Logarithms. Ex: Converting an exponential to logarithmic statement. Evaluating logarithms. Fancier logarithm expressions. Evaluating logarithms 2. Graphing Logarithmic Functions. Introduction to Logarithms. Introduction to logarithm properties. Introduction to logarithm properties (part 2). Logarithm of a Power. Sum of Logarithms with Same Base. Using Multiple Logarithm Properties to Simplify. Operations with logarithms. Change of Base Formula. Proof: log a + log b = log ab. Proof: A(log B) = log (B^A), log A - log B = log (A/B). Change of base formula proof. Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Logarithmic Scale. Richter Scale. Natural Logarithm with a Calculator. Calculator for Natural Logarithms. Graphing Natural Logarithm Function. Logarithms. Ex: Converting an exponential to logarithmic statement. Evaluating logarithms. Fancier logarithm expressions. Evaluating logarithms 2. Graphing Logarithmic Functions. Introduction to Logarithms. Introduction to logarithm properties. Introduction to logarithm properties (part 2). Logarithm of a Power. Sum of Logarithms with Same Base. Using Multiple Logarithm Properties to Simplify. Operations with logarithms. Change of Base Formula. Proof: log a + log b = log ab. Proof: A(log B) = log (B^A), log A - log B = log (A/B). Change of base formula proof. Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Logarithmic Scale. Richter Scale. Natural Logarithm with a Calculator. Calculator for Natural Logarithms. Graphing Natural Logarithm Function.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.