Online courses directory (237)
Mathematics is about structure, about reasoning, and about modeling. This course braids these three threads together. Mathematical logic began as the study of the reasoning used in mathematics, but it turns out to be useful in describing the mathematical concept of structure and in modeling automated reasoningthat is, modeling computation. The logical approach to structure gives an alternate perspective on such other mathematical subjects as combinatorics and abstract algebra. This, for the most part, is described by the area of model theory, which is the focus of Unit 1. In Unit 2, we will look at modeling computation. The central fact of these models, from a logical standpoint, is that once we can handle a computation as a definable mathematical object, we can prove that certain computations are impossible. The most famous such proof is Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorem, showing that it is impossible to compute truth in a system sufficiently strong to describe natural number arithmetic.
This course will introduce you to a number of statistical tools and techniques that are routinely used by modern statisticians for a wide variety of applications. First, we will review basic knowledge and skills that you learned in MA121: Introduction to Statistics [1]. Units 2-5 will introduce you to new ways to design experiments and to test hypotheses, including multiple and nonlinear regression and nonparametric statistics. You will learn to apply these methods to building models to analyze complex, multivariate problems. You will also learn to write scripts to carry out these analyses in R, a powerful statistical programming language. The last unit is designed to give you a grand tour of several advanced topics in applied statistics. [1] http://www.saylor.org/courses/ma121/…
Logic is a remarkable discipline. It is deeply tied to mathematics and philosophy, as correctness of argumentation is particularly crucial for these abstract disciplines. Logic systematizes and analyzes steps in reasoning: correct steps guarantee the truth of their conclusion given the truth of their premise(s); incorrect steps allow the formulation of counterexamples, i.e., of situations in which the premises are true, but the conclusion is false. Recognizing (and having conceptual tools for recognizing) the correctness or incorrectness of steps is crucial in order to critically evaluate arguments, not just in philosophy and mathematics, but also in ordinary life. This skill is honed by working in two virtual labs. In the ProofLab you learn to construct complex arguments in a strategically guided way, whereas in the TruthLab the emphasis is on finding counterexamples systematically. Who Should Take This Course? This is an introductory course designed for students from a broad range of disciplines, from mathematics and computer science to drama and creative writing. The highly interactive presentation makes it possible for any student to master the material. Concise multimedia lectures introduce each chapter; they discuss, in detail, the central notions and techniques presented in the text, but also articulate and motivate the learning objectives for each chapter. Open & Free Version The Open & Free, Logic & Proofs course includes the first five chapters of Logic & Proofs, providing a basic introduction to sentential logic. A full version of Logic & Proofs, including both sentential and predicate logic, is also available without technical or instructor support to independent users, for a small fee. No credit is awarded for completing either the Open & Free, Logic & Proofs course or the full, unsupported Logic & Proofs course. Academic Version Academic use of Logic & Proofs provides a full course on modern symbolic logic, covering both sentential and predicate logic, with identity. Optional suites of exams are available for use in academic sections.
This introductory mathematics course is for you if you have a solid foundation in arithmetic (that is, you know how to perform operations with real numbers, including negative numbers, fractions, and decimals). Numbers and basic arithmetic are used often in everyday life in both simple situations, like estimating how much change you will get when making a purchase in a store, as well as in more complicated ones, like figuring out how much time it would take to pay off a loan under interest. The subject of algebra focuses on generalizing these procedures. For example, algebra will enable you to describe how to calculate change without specifying how much money is to be spent on a purchase-it will teach you the basic formulas and steps you need to take no matter what the specific details of the situation are. Likewise, accountants use algebraic formulas to calculate the monthly loan payments for a loan of any size under any interest rate. In this course, you will learn how to work with formulas that a…
Partial differential equations (PDEs) describe the relationships among the derivatives of an unknown function with respect to different independent variables, such as time and position. For example, the heat equation can be used to describe the change in heat distribution along a metal rod over time. PDEs arise as part of the mathematical modeling of problems connected to different branches of science, such as physics, biology, and chemistry. In these fields, experiment and observation provide information about the connections between rates of change of an important quantity, such as heat, with respect to different variables. These connections must be exploited to find an explicit way of calculating the unknown quantity, given the values of the independent variables that is, to derive certain laws of nature. While we do not know why partial differential equations provide what has been termed the “unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics in the natural sciences” (the title of a 1960 paper by physicist…
This course is a continuation of MA001: Beginning Algebra [1]. Algebra allows us to formulate real-world problems in an abstract mathematical term or equation. These equations can then be solved by using techniques you will learn in this course. For example, if I can ride my bicycle at 5 miles per hour and I live 12 miles from work, how long will it take me to get to work? Or, suppose I am a pitcher for the St. Louis Cardinals and my fast ball is 95 miles per hour, how much time does the hitter have to react to the baseball? And, can you explain why an object thrown up into the air will come back down? If so, can you tell how long it will take for the object to hit the ground? These are all examples of problems that can be stated as an algebraic equation and then solved. In this course you will study compound inequalities and solve systems of linear equations. You will then study radicals and rational exponents, followed by quadratic equations and techniques used to solve these equations. Finally, you will…
Improve your understanding of data and learn how to develop graphs and charts so you can use this information to make better decisions.
Solve problems using Mathematics, Computer Science and more!. Introduction. The Discovery. Clue #1. Clue #2. Clue #3. Crypto Checkpoint 1. Clue #4. Checkpoint. Crypto Checkpoint 2. Crypto Checkpoint 3. What's Next?. Introduction. The Discovery. Clue #1. Clue #2. Clue #3. Crypto Checkpoint 1. Clue #4. Checkpoint. Crypto Checkpoint 2. Crypto Checkpoint 3. What's Next?.
Learn to tell time with some fun exercises!. Telling time exercise example 1. Telling time exercise example 2. Telling time exercise example 1. Telling time exercise example 2.
Conditional statements and deductive reasoning. Conditional statements exercise examples. Logical argument and deductive reasoning exercise example. Conditional statements and deductive reasoning. Conditional statements exercise examples. Logical argument and deductive reasoning exercise example.
Let's think more visually about things like shifts, rotations, scaling and symmetry. Axis of symmetry. Translations of polygons. Determining a translation for a shape. Rotation of polygons example. Axis of symmetry. Translations of polygons. Determining a translation for a shape. Rotation of polygons example.
En temelinden en zorlarına kadar 2. derece denklemlerle ilgili herşeyi öğreneceksiniz.
2. Dereceden Eşitsizliklerle ilgili bilmeniz gereken her şeyi bu derste bulacaksınız.
Precalculus I is designed to prepare you for Precalculus II, Calculus, Physics, and higher math and science courses. In this course, the main focus is on five types of functions: linear, polynomial, rational, exponential, and logarithmic. In accompaniment with these functions, you will learn how to solve equations and inequalities, graph, find domains and ranges, combine functions, and solve a multitude of real-world applications. In this course, you will not only be learning new algebraic techniques that are necessary for other math and science courses, but you will be learning to become a critical thinker. You will be able to determine what is the best approach to take such as numerical, graphical, or algebraic to solve a problem given particular information. Then you will investigate and solve the problem, interpret the answer, and determine if it is reasonable. A few examples of applications in this course are determining compound interest, growth of bacteria, decay of a radioactive substance, and the…
What ratios and proportions are. Using them to solve problems in the real world. Ratio problem with basic algebra (new HD). Writing proportions. Writing proportions. Find an Unknown in a Proportion. Find an Unknown in a Proportion 2. Proportions 1. Proportions 2 exercise examples. Proportions 2. Constructing proportions to solve application problems. Constructing proportions to solve application problems. The Golden Ratio. Advanced ratio problems. More advanced ratio problem--with Algebra (HD version). Another Take on the Rate Problem. Alternate Solution to Ratio Problem (HD Version). Mountain height word problem. Ratio problem with basic algebra (new HD). Writing proportions. Writing proportions. Find an Unknown in a Proportion. Find an Unknown in a Proportion 2. Proportions 1. Proportions 2 exercise examples. Proportions 2. Constructing proportions to solve application problems. Constructing proportions to solve application problems. The Golden Ratio. Advanced ratio problems. More advanced ratio problem--with Algebra (HD version). Another Take on the Rate Problem. Alternate Solution to Ratio Problem (HD Version). Mountain height word problem.
This topic will add a ton of tools to your algebraic toolbox. You'll be able to multiply any expression and learn to factor a bunch a well. This will allow you to solve a broad array of problems in algebra. Factoring Special Products. Example 1: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 1. Example 2: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 2. Factoring to produce difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 3. Example: Factoring perfect square trinomials. Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression. Example: Factoring special products. Multiplying Monomials. Dividing Monomials. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 1. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 2. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 3. Monomial Greatest Common Factor. Multiplying binomials word problem. FOIL for multiplying binomials. Multiplying Binomials with Radicals. Multiplying binomials example 1. FOIL method for multiplying binomials example 2. Square a Binomial. Special Products of Binomials. Multiplying binomials to get difference of squares. Squaring a binomial. Multiplying expressions 0.5. Squaring a binomial example 2. Classic multiplying binomials video. Multiplying expressions 1. Factoring and the Distributive Property 3. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring and the Distributive Property. Factoring and the Distributive Property 2. Factor expressions using the GCF. Factoring quadratic expressions. Examples: Factoring simple quadratics. Example 1: Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring polynomials 1. Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor. Factoring polynomials 2. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Example: Basic grouping. Example 1: Factoring by grouping. Example 2: Factoring by grouping. Example 3: Factoring by grouping. Example 4: Factoring by grouping. Example 5: Factoring by grouping. Example 6: Factoring by grouping. Factoring polynomials by grouping. Factoring quadratics with two variables. Factoring quadratics with two variables example. Factoring polynomials with two variables. Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial. Interesting Polynomial Coefficient Problem. Polynomials1. Polynomials 2. Evaluating a polynomial at a given value. Simplify a polynomial. Adding Polynomials. Example: Adding polynomials with multiple variables. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 1. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 2. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 3. Subtracting Polynomials. Subtracting polynomials with multiple variables. Adding and subtracting polynomials. Multiplying Monomials by Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials 3. More multiplying polynomials. Multiplying polynomials. Polynomial Division. Polynomial divided by monomial. Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial. Dividing polynomials 1. Dividing polynomials with remainders. Synthetic Division. Synthetic Division Example 2. Why Synthetic Division Works. Factoring Sum of Cubes. Difference of Cubes Factoring. Algebraic Long Division. Algebra II: Simplifying Polynomials. Factoring Special Products. Example 1: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 1. Example 2: Factoring difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 2. Factoring to produce difference of squares. Factoring difference of squares 3. Example: Factoring perfect square trinomials. Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression. Example: Factoring special products. Multiplying Monomials. Dividing Monomials. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 1. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 2. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 3. Monomial Greatest Common Factor. Multiplying binomials word problem. FOIL for multiplying binomials. Multiplying Binomials with Radicals. Multiplying binomials example 1. FOIL method for multiplying binomials example 2. Square a Binomial. Special Products of Binomials. Multiplying binomials to get difference of squares. Squaring a binomial. Multiplying expressions 0.5. Squaring a binomial example 2. Classic multiplying binomials video. Multiplying expressions 1. Factoring and the Distributive Property 3. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring linear binomials. Factoring and the Distributive Property. Factoring and the Distributive Property 2. Factor expressions using the GCF. Factoring quadratic expressions. Examples: Factoring simple quadratics. Example 1: Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring polynomials 1. Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor. Factoring polynomials 2. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Example: Basic grouping. Example 1: Factoring by grouping. Example 2: Factoring by grouping. Example 3: Factoring by grouping. Example 4: Factoring by grouping. Example 5: Factoring by grouping. Example 6: Factoring by grouping. Factoring polynomials by grouping. Factoring quadratics with two variables. Factoring quadratics with two variables example. Factoring polynomials with two variables. Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial. Interesting Polynomial Coefficient Problem. Polynomials1. Polynomials 2. Evaluating a polynomial at a given value. Simplify a polynomial. Adding Polynomials. Example: Adding polynomials with multiple variables. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 1. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 2. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 3. Subtracting Polynomials. Subtracting polynomials with multiple variables. Adding and subtracting polynomials. Multiplying Monomials by Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials. Multiplying Polynomials 3. More multiplying polynomials. Multiplying polynomials. Polynomial Division. Polynomial divided by monomial. Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial. Dividing polynomials 1. Dividing polynomials with remainders. Synthetic Division. Synthetic Division Example 2. Why Synthetic Division Works. Factoring Sum of Cubes. Difference of Cubes Factoring. Algebraic Long Division. Algebra II: Simplifying Polynomials.
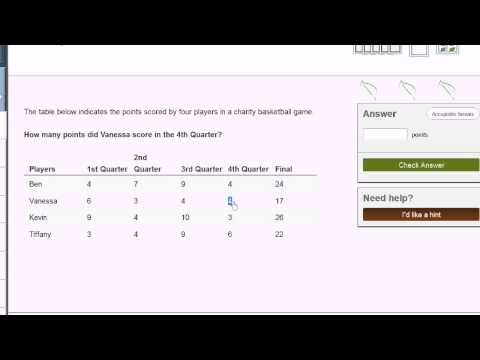
You already have many tools in your mathematical toolkit. In this topic, you'll use these in settings that you're likely to encounter in the real world!. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 2. Reading tables 2. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading Pictographs. Reading pictographs 1. Reading pictographs 2. Reading Bar Graphs. Histograms. Reading bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 3. Reading bar charts 3. Reading Line Graphs. Reading line charts 1. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Multistep word problems example 1). Multistep word problems example 2). Multistep word problems example 3). Multistep equations without variables. Greater than and less than symbols. Comparing whole numbers. Plotting inequalities on a number line. Writing numerical inequalities exercise. Writing numerical inequalities. Inequalities in one variable 1 exercise. Inequalities in one variable 1. Inequalities on a number line. Inequalities on a number line. Rational number word problem example 1. Rational number word problem example 2. Rational number word problem example 3. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Rational number word problems. Figuring out days of the week. Math patterns example 1. Math patterns example 2. Math patterns. Relationships between patterns. Interpreting relationships between patterns. Interpreting and graphing relationships between patterns. Visualizing and interpreting relationships between patterns. Constructing numerical expressions example. Evaluating an expression with and without parentheses. Expressions with parentheses. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 1. Reading tables 2. Reading tables 2. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading stem and leaf plots. Reading Pictographs. Reading pictographs 1. Reading pictographs 2. Reading Bar Graphs. Histograms. Reading bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Creating bar charts 1. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 2. Reading bar charts 3. Reading bar charts 3. Reading Line Graphs. Reading line charts 1. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Multistep word problems example 1). Multistep word problems example 2). Multistep word problems example 3). Multistep equations without variables. Greater than and less than symbols. Comparing whole numbers. Plotting inequalities on a number line. Writing numerical inequalities exercise. Writing numerical inequalities. Inequalities in one variable 1 exercise. Inequalities in one variable 1. Inequalities on a number line. Inequalities on a number line. Rational number word problem example 1. Rational number word problem example 2. Rational number word problem example 3. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Rational number word problems. Figuring out days of the week. Math patterns example 1. Math patterns example 2. Math patterns. Relationships between patterns. Interpreting relationships between patterns. Interpreting and graphing relationships between patterns. Visualizing and interpreting relationships between patterns. Constructing numerical expressions example. Evaluating an expression with and without parentheses. Expressions with parentheses.
This course is taught in French Vous voulez comprendre l'arithmétique ? Vous souhaitez découvrir une application des mathématiques à la vie quotidienne ? Ce cours est fait pour vous ! De niveau première année d'université, vous apprendrez les bases de l'arithmétique (division euclidienne, théorème de Bézout, nombres premiers, congruence). Vous vous êtes déjà demandé comment sont sécurisées les transactions sur Internet ? Vous découvrirez les bases de la cryptographie, en commençant par les codes les plus simples pour aboutir au code RSA. Le code RSA est le code utilisé pour crypter les communications sur internet. Il est basé sur de l'arithmétique assez simple que l'on comprendra en détail. Vous pourrez en plus mettre en pratique vos connaissances par l'apprentissage de notions sur le langage de programmation Python. Vous travaillerez à l'aide de cours écrits et de vidéos, d'exercices corrigés en vidéos, des quiz, des travaux pratiques. Le cours est entièrement gratuit !
2003 AIME II Problem 1. 2003 AIME II Problem 3. Sum of factors of 27000. Sum of factors 2. 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 5. 2003 AIME II Problem 5 Minor Correction. Area Circumradius Formula Proof. 2003 AIME II Problem 6. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Sum of Polynomial Roots (Proof). Sum of Squares of Polynomial Roots. 2003 AIME II Problem 9. 2003 AIME II Problem 10. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 12. 2003 AIME II Problem 13. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 3). 2003 AIME II Problem 1. 2003 AIME II Problem 3. Sum of factors of 27000. Sum of factors 2. 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 4 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 5. 2003 AIME II Problem 5 Minor Correction. Area Circumradius Formula Proof. 2003 AIME II Problem 6. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. 2003 AIME II Problem 8. Sum of Polynomial Roots (Proof). Sum of Squares of Polynomial Roots. 2003 AIME II Problem 9. 2003 AIME II Problem 10. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 12. 2003 AIME II Problem 13. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 1). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 2). 2003 AIME II Problem 15 (part 3).
The AMC 10 is part of the series of contests administered by the MAA American Mathematics Competitions that determines the United States team in the International Math Olympiad. The AMC 10 is a 25 question, 75 minute multiple choice test for students in 10th grade or below. Two versions of the AMC 10 are offered each year. 2013 AMC 10 A #21 / AMC 12 A #17. 2013 AMC 10 A #22 / AMC 12 A #18. 2013 AMC 10 A #23 / AMC 12 A #19. 2013 AMC 10 A #24. 2013 AMC 10 A #25. 2013 AMC 10 A #21 / AMC 12 A #17. 2013 AMC 10 A #22 / AMC 12 A #18. 2013 AMC 10 A #23 / AMC 12 A #19. 2013 AMC 10 A #24. 2013 AMC 10 A #25.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.