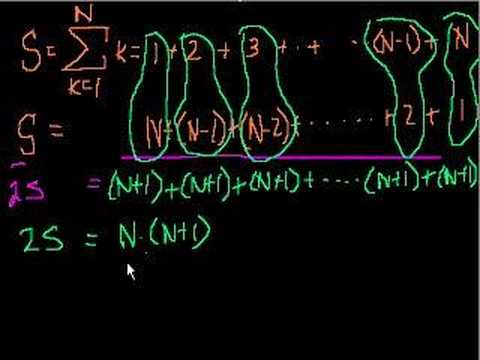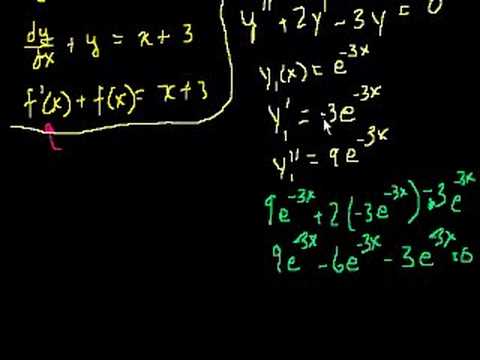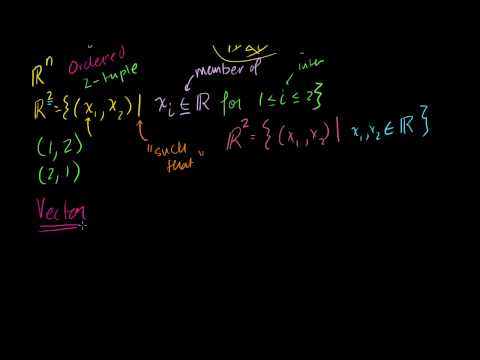Online courses directory (237)
We explore creating and moving between various coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems.
Linear differential equations that contain second derivatives. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4.
Throughout this course, we will use algebra to quantify and describe the world around us. Have you ever wondered how many songs can fit onto your flash drive? By the end of the course, you’ll have stronger skills for modeling problems, analyzing patterns, and using algebra to arrive at conclusions.
Sample questions from the A.P. Calculus AB and BC exams (both multiple choice and free answer). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1 parts b c d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (c & d). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (c). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4c. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5c.. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 a. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 b&c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 c&d. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 d. Calculus BC 2008 2 a. Calculus BC 2008 2 b &c. Calculus BC 2008 2d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6c. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #1 parts b c d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #2 (c & d). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (a & b). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #3 (c). 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4c. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #4d. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #5c.. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus AB Free Response #6c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 a. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 b&c. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 c&d. AP Calculus BC Exams: 2008 1 d. Calculus BC 2008 2 a. Calculus BC 2008 2 b &c. Calculus BC 2008 2d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #1d. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #3 (b & c). 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6a. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6b. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6c. 2011 Calculus BC Free Response #6d.
Volume under a surface with double integrals. Triple integrals as well. Double Integral 1. Double Integrals 2. Double Integrals 3. Double Integrals 4. Double Integrals 5. Double Integrals 6. Triple Integrals 1. Triple Integrals 2. Triple Integrals 3. Double Integral 1. Double Integrals 2. Double Integrals 3. Double Integrals 4. Double Integrals 5. Double Integrals 6. Triple Integrals 1. Triple Integrals 2. Triple Integrals 3.
Random variables. Expected value. Probability distributions (both discrete and continuous). Binomial distribution. Poisson processes. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Expected value. Law of Large Numbers. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Galton Board Exploration. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Expected value. Law of Large Numbers. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Galton Board Exploration. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2.
Transforms and the Laplace transform in particular. Convolution integrals. Laplace Transform 1. Laplace Transform 2. L{sin(at)}) - transform of sin(at). Part 2 of the transform of the sin(at). Laplace as linear operator and Laplace of derivatives. Laplace Transform of cos t and polynomials. "Shifting" transform by multiplying function by exponential. Laplace Transform of : L{t}. Laplace Transform of t^n: L{t^n}. Laplace Transform of the Unit Step Function. Inverse Laplace Examples. Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform of the Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform to solve an equation. Laplace Transform solves an equation 2. Using the Laplace Transform to solve a nonhomogeneous eq. Laplace/Step Function Differential Equation. Introduction to the Convolution. The Convolution and the Laplace Transform. Using the Convolution Theorem to Solve an Initial Value Prob. Laplace Transform 1. Laplace Transform 2. L{sin(at)}) - transform of sin(at). Part 2 of the transform of the sin(at). Laplace as linear operator and Laplace of derivatives. Laplace Transform of cos t and polynomials. "Shifting" transform by multiplying function by exponential. Laplace Transform of : L{t}. Laplace Transform of t^n: L{t^n}. Laplace Transform of the Unit Step Function. Inverse Laplace Examples. Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform of the Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform to solve an equation. Laplace Transform solves an equation 2. Using the Laplace Transform to solve a nonhomogeneous eq. Laplace/Step Function Differential Equation. Introduction to the Convolution. The Convolution and the Laplace Transform. Using the Convolution Theorem to Solve an Initial Value Prob.
Line integral of scalar and vector-valued functions. Green's theorem and 2-D divergence theorem. Introduction to the Line Integral. Line Integral Example 1. Line Integral Example 2 (part 1). Line Integral Example 2 (part 2). Position Vector Valued Functions. Derivative of a position vector valued function. Differential of a vector valued function. Vector valued function derivative example. Line Integrals and Vector Fields. Using a line integral to find the work done by a vector field example. Parametrization of a Reverse Path. Scalar Field Line Integral Independent of Path Direction. Vector Field Line Integrals Dependent on Path Direction. Path Independence for Line Integrals. Closed Curve Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields. Example of Closed Line Integral of Conservative Field. Second Example of Line Integral of Conservative Vector Field. Green's Theorem Proof Part 1. Green's Theorem Proof (part 2). Green's Theorem Example 1. Green's Theorem Example 2. Constructing a unit normal vector to a curve. 2 D Divergence Theorem. Conceptual clarification for 2-D Divergence Theorem. Introduction to the Line Integral. Line Integral Example 1. Line Integral Example 2 (part 1). Line Integral Example 2 (part 2). Position Vector Valued Functions. Derivative of a position vector valued function. Differential of a vector valued function. Vector valued function derivative example. Line Integrals and Vector Fields. Using a line integral to find the work done by a vector field example. Parametrization of a Reverse Path. Scalar Field Line Integral Independent of Path Direction. Vector Field Line Integrals Dependent on Path Direction. Path Independence for Line Integrals. Closed Curve Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields. Example of Closed Line Integral of Conservative Field. Second Example of Line Integral of Conservative Vector Field. Green's Theorem Proof Part 1. Green's Theorem Proof (part 2). Green's Theorem Example 1. Green's Theorem Example 2. Constructing a unit normal vector to a curve. 2 D Divergence Theorem. Conceptual clarification for 2-D Divergence Theorem.
Sequences, series and approximating functions. Maclaurin and Taylor series. Sequences and Series (part 1). Sequences and series (part 2). Maclaurin and Taylor Series Intuition. Cosine Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin). Sine Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin). Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin) for e to the x. Euler's Formula and Euler's Identity. Visualizing Taylor Series Approximations. Generalized Taylor Series Approximation. Visualizing Taylor Series for e^x. Error or Remainder of a Taylor Polynomial Approximation. Proof: Bounding the Error or Remainder of a Taylor Polynomial Approximation. Polynomial approximation of functions (part 1). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 2). Approximating functions with polynomials (part 3). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 4). Polynomial approximations of functions (part 5). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 6). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 7). Taylor Polynomials. Sequences and Series (part 1). Sequences and series (part 2). Maclaurin and Taylor Series Intuition. Cosine Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin). Sine Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin). Taylor Series at 0 (Maclaurin) for e to the x. Euler's Formula and Euler's Identity. Visualizing Taylor Series Approximations. Generalized Taylor Series Approximation. Visualizing Taylor Series for e^x. Error or Remainder of a Taylor Polynomial Approximation. Proof: Bounding the Error or Remainder of a Taylor Polynomial Approximation. Polynomial approximation of functions (part 1). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 2). Approximating functions with polynomials (part 3). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 4). Polynomial approximations of functions (part 5). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 6). Polynomial approximation of functions (part 7). Taylor Polynomials.
Differential equations with only first derivatives. What is a differential equation. Simple Differential Equations. Separable Differential Equations. Separable differential equations 2. Exact Equations Intuition 1 (proofy). Exact Equations Intuition 2 (proofy). Exact Equations Example 1. Exact Equations Example 2. Exact Equations Example 3. Integrating factors 1. Integrating factors 2. First order homegenous equations. First order homogeneous equations 2. What is a differential equation. Simple Differential Equations. Separable Differential Equations. Separable differential equations 2. Exact Equations Intuition 1 (proofy). Exact Equations Intuition 2 (proofy). Exact Equations Example 1. Exact Equations Example 2. Exact Equations Example 3. Integrating factors 1. Integrating factors 2. First order homegenous equations. First order homogeneous equations 2.
Fitting a line to points. Linear regression. R-squared. Correlation and Causality. Fitting a Line to Data. Estimating the line of best fit exercise. Estimating the line of best fit. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line. Correlation and Causality. Fitting a Line to Data. Estimating the line of best fit exercise. Estimating the line of best fit. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line.
Introduction to probability. Independent and dependent events. Compound events. Mutual exclusive events. Addition rule for probability. Basic Probability. Probability space exercise example. Probability space. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Probability 1. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Independent probability. Frequency Stability. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Dependent probability. Monty Hall Problem. Intersection and union of sets. Relative complement or difference between sets. Universal set and absolute complement. Subset, strict subset, and superset. Bringing the set operations together. Basic set notation. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8). Introduction to Random Variables. Basic Probability. Probability space exercise example. Probability space. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Probability 1. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Independent probability. Frequency Stability. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Dependent probability. Monty Hall Problem. Intersection and union of sets. Relative complement or difference between sets. Universal set and absolute complement. Subset, strict subset, and superset. Bringing the set operations together. Basic set notation. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8). Introduction to Random Variables.
Using definite integrals with the shell and disc methods to find volumes of solids of revolution. Disk method around x-axis. Generalizing disc method around x-axis. Disc method around y-axis. Disc method (washer method) for rotation around x-axis. Generalizing the washer method. Disc method rotation around horizontal line. Washer method rotating around non-axis. Part 2 of washer for non axis rotation. Disc method rotating around vertical line. Calculating integral disc method around vertical line. Washer or ring method for vertical line rotation. Evaluating integral for washer method around vertical line. Shell method for rotating around vertical line. Evaluating integral for shell method example. Shell method for rotating around horizontal line. Shell method with two functions of x. Calculating integral with shell method. Shell method with two functions of y. Part 2 of shell method with 2 functions of y. Disc method: function rotated about x-axis. Disc method (rotating f(x) about x axis). Volume of a sphere. Disc method with outer and inner function boundaries. Shell method to rotate around y-axis. Disk method: rotating x=f(y) around the y-axis. Shell method around a non-axis line. Shell method around a non-axis line 2. Disk method around x-axis. Generalizing disc method around x-axis. Disc method around y-axis. Disc method (washer method) for rotation around x-axis. Generalizing the washer method. Disc method rotation around horizontal line. Washer method rotating around non-axis. Part 2 of washer for non axis rotation. Disc method rotating around vertical line. Calculating integral disc method around vertical line. Washer or ring method for vertical line rotation. Evaluating integral for washer method around vertical line. Shell method for rotating around vertical line. Evaluating integral for shell method example. Shell method for rotating around horizontal line. Shell method with two functions of x. Calculating integral with shell method. Shell method with two functions of y. Part 2 of shell method with 2 functions of y. Disc method: function rotated about x-axis. Disc method (rotating f(x) about x axis). Volume of a sphere. Disc method with outer and inner function boundaries. Shell method to rotate around y-axis. Disk method: rotating x=f(y) around the y-axis. Shell method around a non-axis line. Shell method around a non-axis line 2.
Divergence theorem intuition. Divergence theorem examples and proofs. Types of regions in 3D. 3-D Divergence Theorem Intuition. Divergence Theorem Example 1. Why we got zero flux in Divergence Theorem Example 1. Type I Regions in Three Dimensions. Type II Regions in Three Dimensions. Type III Regions in Three Dimensions. Divergence Theorem Proof (part 1). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 2). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 3). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 4). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 5). 3-D Divergence Theorem Intuition. Divergence Theorem Example 1. Why we got zero flux in Divergence Theorem Example 1. Type I Regions in Three Dimensions. Type II Regions in Three Dimensions. Type III Regions in Three Dimensions. Divergence Theorem Proof (part 1). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 2). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 3). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 4). Divergence Theorem Proof (part 5).
We live in a time of unprecedented access to information. You'll learn how to use statistics to interpret that information and make decisions. San Jose State University
Let's get our feet wet by thinking in terms of vectors and spaces. Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Scaling vectors. Adding vectors. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A). Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Scaling vectors. Adding vectors. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A).
We've always been communicating.... as we moved from signal fires, to alphabets & electricity the problems remained the same. What is Information Theory?. Prehistory: Proto-writing. Ptolemaic: Rosetta Stone. Ancient History: The Alphabet. Source Encoding. Visual Telegraphs (case study). Decision Tree Exploration. Electrostatic Telegraphs (case study). The Battery & Electromagnetism. Morse Code & The Information Age. Morse code Exploration. What's Next?. Symbol Rate. Symbol Rate Exploration. Introduction to Channel Capacity. Message Space Exploration. Measuring Information. Galton Board Exploration. Origin of Markov Chains. Markov Chain Exploration. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Markov Text Exploration. What's Next?. What is Information Theory?. Prehistory: Proto-writing. Ptolemaic: Rosetta Stone. Ancient History: The Alphabet. Source Encoding. Visual Telegraphs (case study). Decision Tree Exploration. Electrostatic Telegraphs (case study). The Battery & Electromagnetism. Morse Code & The Information Age. Morse code Exploration. What's Next?. Symbol Rate. Symbol Rate Exploration. Introduction to Channel Capacity. Message Space Exploration. Measuring Information. Galton Board Exploration. Origin of Markov Chains. Markov Chain Exploration. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Markov Text Exploration. What's Next?.
Thinking about forms of derivatives in multi-dimensions and for vector-valued functions: partial derivatives, gradient, divergence and curl. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives 2. Gradient 1. Gradient of a scalar field. Divergence 1. Divergence 2. Divergence 3. Curl 1. Curl 2. Curl 3. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives 2. Gradient 1. Gradient of a scalar field. Divergence 1. Divergence 2. Divergence 3. Curl 1. Curl 2. Curl 3.
Math is everywhere. In this class, you’ll gain an in-depth understanding of algebraic principles, many of which you may have seen before, and learn how to use them to solve problems that we encounter in everyday life. The online version of College Algebra will cover all of the topics that you would see in more traditional class formats, but it will present the material in a way that we hope you’ll find fresh and interesting. You will learn about functions, polynomials, graphing, complex numbers, exponential and logarithmic equations, and much more, all through exploring real-world scenarios.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.