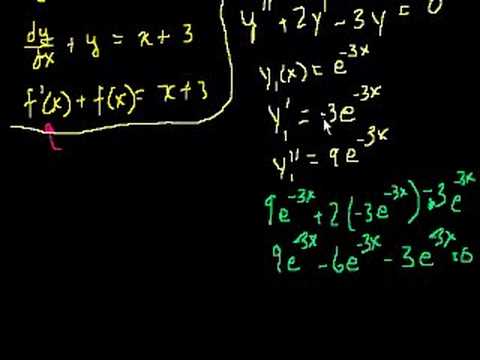Online courses directory (237)
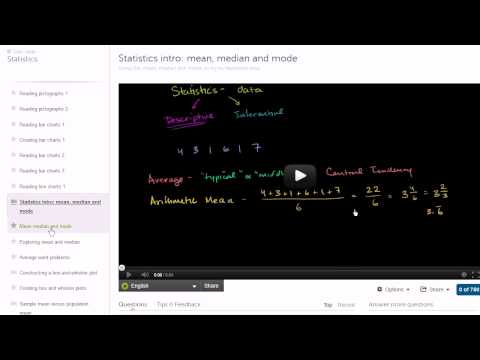
Introduction to statistics. We start with the basics of reading and interpretting data and then build into descriptive and inferential statistics that are typically covered in an introductory course on the subject. Overview of Khan Academy statistics. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Sample mean versus population mean.. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Introduction to Random Variables. Probability Density Functions. Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value: E(X). Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. Law of Large Numbers. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Type 1 Errors. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Squared Error of Regression Line. Proof (Part 1) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof Part 2 Minimizing Squared Error to Line. Proof (Part 3) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Proof (Part 4) Minimizing Squared Error to Regression Line. Regression Line Example. Second Regression Example. R-Squared or Coefficient of Determination. Calculating R-Squared. Covariance and the Regression Line. Correlation and Causality. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Mean Median and Mode. Range and Mid-range. Reading Pictographs. Reading Bar Graphs. Reading Line Graphs. Reading Pie Graphs (Circle Graphs). Misleading Line Graphs. Stem-and-leaf Plots. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance. Deductive Reasoning 1. Deductive Reasoning 2. Deductive Reasoning 3. Inductive Reasoning 1. Inductive Reasoning 2. Inductive Reasoning 3. Inductive Patterns.
Solving and writing algebraic ratios and proportions. Solving rational equations. Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Understanding Proportions. Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Find an Unknown in a Proportion. Ratio and Proportion. Find an Unknown in a Proportion 2. Another Take on the Rate Problem. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Writing Proportions. Ratio problem with basic algebra (new HD). More advanced ratio problem--with Algebra (HD version). Alternate Solution to Ratio Problem (HD Version). Advanced ratio problems. Unit conversion. Conversion between metric units. Converting within the metric system. Converting pounds to ounces. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting Farenheit to Celsius. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales. Applying the Metric System. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting Yards into Inches. Unit Conversion with Fractions. Performing arithmetic calculations on units of volume. Application problems involving units of weight. Solving application problems involving units of volume. Unit Conversion Example: Drug Dosage. Perimeter and Unit Conversion. Rational Equations. Solving Rational Equations 1. Solving Rational Equations 2. Solving Rational Equations 3. Applying Rational Equations 1. Applying Rational Equations 2. Applying Rational Equations 3. Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations. Rational Inequalities 2.
Defining and using the commutative, associative, distributive, identity, and inverse properties. Commutative Law of Addition. Commutative Law of Multiplication. Associative Law of Addition. Associative Law of Multiplication. Commutative Property for Addition. The Distributive Property. The Distributive Property 2. Distributive Property Example 1. CA Algebra I: Number Properties and Absolute Value. Identity Property of 1. Identity property of 1 (second example). Identity property of 0. Inverse Property of Addition. Inverse Property of Multiplication. Why Dividing by Zero is Undefined. Why Zero Divided by Zero is Undefined/Indeterminate. Undefined and Indeterminate.
Solving and writing ratios and proportions without algebra. Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Understanding Proportions. Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Find an Unknown in a Proportion 2. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Unit conversion. Converting units of length. Conversion between metric units. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting within the metric system. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting pounds to ounces. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius. Speed translation.
Identifying types of quadrilaterals, finding measurements, and applying and proving postulates. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of a Regular Hexagon. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Rhombus Diagonals. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Area of a Regular Hexagon. Problem involving angle derived from square and circle. 2003 AIME II Problem 7. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures.
Random logic puzzles and brain teasers. Fun to do and useful for many job interviews!. Liar Truth-teller Brain Teaser. Toggler Brain Teaser. Alien Abduction Brain Teaser. Blue Forehead Room Brain Teaser. Blue Forehead Room Solution. Forehead Numbers Brain Teaser. Light Bulb Switching Brain Teaser. Path Counting Brain Teaser. 3-D Path Counting Brain Teaser. Liar Truth-teller Brain Teaser. Toggler Brain Teaser. Alien Abduction Brain Teaser. Blue Forehead Room Brain Teaser. Blue Forehead Room Solution. Forehead Numbers Brain Teaser. Light Bulb Switching Brain Teaser. Path Counting Brain Teaser. 3-D Path Counting Brain Teaser.
Identifying, solving, and graphing various types of functions. What is a function. Difference between Equations and Functions. Function example problems. Ex: Constructing a function. Understanding Function Notation Example 1). Understanding Function Notation Example 2). Understanding Function Notation Example 3). Understanding function notation. Testing if a relationship is a function. Graphical Relations and Functions. Functions as Graphs. Recognizing functions (example 1). Recognizing functions (example 2). Recognizing functions. Relations and Functions. Functional Relationships 1. Recognizing functions (example 3). Recognizing functions (example 4). Recognizing functions (example 5). Recognizing functions 2. Domain of a function. Domain and Range of a Relation. Domain and Range of a Function Given a Formula. Domain and Range 1. Domain of a Radical Function. Domain of a function. Domain and Range 2. Domain and Range of a Function. Range of a function. Domain and range from graphs. Domain and range from graph. Direct and Inverse Variation. Recognizing Direct and Inverse Variation. Proportionality Constant for Direct Variation. Direct and inverse variation. Direct Variation Models. Direct Variation 1. Inverse Variation Application. Direct Inverse and Joint Variation. Direct Variation Application. Ex 1: Evaluating a function. Ex 2: Graphing a basic function. Graphing a parabola with a table of values. Ex 4: Graphing radical functions. Ex: Graphing exponential functions. Views of a function. Interpreting a graph exercise example. Interpreting graphs of linear and nonlinear functions. Quotient of Functions. Sum of Functions. Product of Functions. Difference of Functions. Evaluating a function expression. Evaluating expressions with function notation. Evaluating composite functions example. Evaluating composite functions. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Inverses of functions. New operator definitions. New operator definitions 1. New operator definitions 2. New operator definitions 2. Introduction to functions. Functions Part 2. Functions (Part III). Functions (part 4). What is a function. Difference between Equations and Functions. Function example problems. Ex: Constructing a function. Understanding Function Notation Example 1). Understanding Function Notation Example 2). Understanding Function Notation Example 3). Understanding function notation. Testing if a relationship is a function. Graphical Relations and Functions. Functions as Graphs. Recognizing functions (example 1). Recognizing functions (example 2). Recognizing functions. Relations and Functions. Functional Relationships 1. Recognizing functions (example 3). Recognizing functions (example 4). Recognizing functions (example 5). Recognizing functions 2. Domain of a function. Domain and Range of a Relation. Domain and Range of a Function Given a Formula. Domain and Range 1. Domain of a Radical Function. Domain of a function. Domain and Range 2. Domain and Range of a Function. Range of a function. Domain and range from graphs. Domain and range from graph. Direct and Inverse Variation. Recognizing Direct and Inverse Variation. Proportionality Constant for Direct Variation. Direct and inverse variation. Direct Variation Models. Direct Variation 1. Inverse Variation Application. Direct Inverse and Joint Variation. Direct Variation Application. Ex 1: Evaluating a function. Ex 2: Graphing a basic function. Graphing a parabola with a table of values. Ex 4: Graphing radical functions. Ex: Graphing exponential functions. Views of a function. Interpreting a graph exercise example. Interpreting graphs of linear and nonlinear functions. Quotient of Functions. Sum of Functions. Product of Functions. Difference of Functions. Evaluating a function expression. Evaluating expressions with function notation. Evaluating composite functions example. Evaluating composite functions. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Inverses of functions. New operator definitions. New operator definitions 1. New operator definitions 2. New operator definitions 2. Introduction to functions. Functions Part 2. Functions (Part III). Functions (part 4).
CA Algebra I: Number Properties and Absolute Value. CA Algebra I: Simplifying Expressions. CA Algebra I: Simple Logical Arguments. CA Algebra I: Graphing Inequalities. CA Algebra I: Slope and Y-intercept. CA Algebra I: Systems of Inequalities. CA Algebra I: Simplifying Expressions. CA Algebra I: Factoring Quadratics. CA Algebra I: Completing the Square. CA Algebra I: Quadratic Equation. CA Algebra I: Quadratic Roots. CA Algebra I: Rational Expressions 1. CA Algebra I: Rational Expressions 2. CA Algebra I: Word Problems. CA Algebra I: More Word Problems. CA Algebra I: Functions.
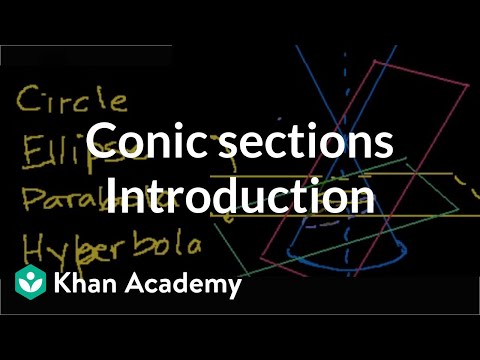
Identifying and graphing circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in factored form. Completing the square to write equation in standard form of a circle. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Shifting and scaling parabolas. Parabola intuition example 1. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in factored form. Completing the square to write equation in standard form of a circle. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Shifting and scaling parabolas. Parabola intuition example 1. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples.
20th century solutions to new problems in Cryptography. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Public Key Cryptography: what is it?. The Discrete Logarithm Problem. Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange. RSA Encryption: step 1. RSA Encryption: step 2. RSA Encryption: step 3. Euler's Totient Function. RSA Encryption: step 4. What should we learn next?.
Recreational mathematics and inspirational videos by resident mathemusician Vi Hart. Doodling in Math: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [1 of 3]. Doodling in Math Class: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [2 of 3]. Doodling in Math: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [Part 3 of 3]. Doodling in Math Class: Binary Trees. Doodling in Math Class: Stars. Doodling in Math Class: Snakes + Graphs. Doodling in Math Class: Infinity Elephants. Doodling in Math: Sick Number Games. Doodling in Math Class: Squiggle Inception. Doodling in Math Class: Triangle Party. Mobius Story: Wind and Mr. Ug. Math Improv: Fruit by the Foot. Wau: The Most Amazing, Ancient, and Singular Number. Are Shakespeare's Plays Encoded within Pi?. What is up with Noises? (The Science and Mathematics of Sound, Frequency, and Pitch). Open Letter to Nickelodeon, Re: SpongeBob's Pineapple under the Sea. How To Snakes. Origami Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. 9.999... reasons that .999... = 1. Pi Is (still) Wrong.. Fractal Fractions. Angle-a-trons. Binary Hand Dance. Re: Visual Multiplication and 48/2(9+3). The Gauss Christmath Special. Rhapsody on the Proof of Pi = 4. Doodle Music. What was up with Pythagoras?. A Song About A Circle Constant. Dialogue for 2. Doodling in Math Class: Connecting Dots. Hexaflexagons. Hexaflexagons 2. Hexaflexagon Safety Guide. Flex Mex. Optimal Potatoes. Green Bean Matherole. Borromean Onion Rings. Thanksgiving Turduckenen-duckenen. Snowflakes, Starflakes, and Swirlflakes. Doodling in Math: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [1 of 3]. Doodling in Math Class: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [2 of 3]. Doodling in Math: Spirals, Fibonacci, and Being a Plant [Part 3 of 3]. Doodling in Math Class: Binary Trees. Doodling in Math Class: Stars. Doodling in Math Class: Snakes + Graphs. Doodling in Math Class: Infinity Elephants. Doodling in Math: Sick Number Games. Doodling in Math Class: Squiggle Inception. Doodling in Math Class: Triangle Party. Mobius Story: Wind and Mr. Ug. Math Improv: Fruit by the Foot. Wau: The Most Amazing, Ancient, and Singular Number. Are Shakespeare's Plays Encoded within Pi?. What is up with Noises? (The Science and Mathematics of Sound, Frequency, and Pitch). Open Letter to Nickelodeon, Re: SpongeBob's Pineapple under the Sea. How To Snakes. Origami Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. 9.999... reasons that .999... = 1. Pi Is (still) Wrong.. Fractal Fractions. Angle-a-trons. Binary Hand Dance. Re: Visual Multiplication and 48/2(9+3). The Gauss Christmath Special. Rhapsody on the Proof of Pi = 4. Doodle Music. What was up with Pythagoras?. A Song About A Circle Constant. Dialogue for 2. Doodling in Math Class: Connecting Dots. Hexaflexagons. Hexaflexagons 2. Hexaflexagon Safety Guide. Flex Mex. Optimal Potatoes. Green Bean Matherole. Borromean Onion Rings. Thanksgiving Turduckenen-duckenen. Snowflakes, Starflakes, and Swirlflakes.
Sal does the 80 problems from the released questions from the California Standards Test for Geometry. Basic understanding of Algebra I necessary. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Challenging Perimeter Problem. CA Geometry: deductive reasoning. CA Geometry: Proof by Contradiction. CA Geometry: More Proofs. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 1. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 2. CA Geometry: More on congruent and similar triangles. CA Geometry: Triangles and Parallelograms. CA Geometry: Area, Pythagorean Theorem. CA Geometry: Area, Circumference, Volume. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Area. CA Geometry: Exterior Angles. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Compass Constructions. CA Geometry: Compass Construction. CA Geometry: Basic Trigonometry. CA Geometry: More Trig. CA Geometry: Circle Area Chords Tangent. CA Geometry: Secants and Translations. Interesting Perimeter and Area Problems. Challenging Perimeter Problem. CA Geometry: deductive reasoning. CA Geometry: Proof by Contradiction. CA Geometry: More Proofs. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 1. CA Geometry: Similar Triangles 2. CA Geometry: More on congruent and similar triangles. CA Geometry: Triangles and Parallelograms. CA Geometry: Area, Pythagorean Theorem. CA Geometry: Area, Circumference, Volume. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Area. CA Geometry: Exterior Angles. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. CA Geometry: Pythagorean Theorem, Compass Constructions. CA Geometry: Compass Construction. CA Geometry: Basic Trigonometry. CA Geometry: More Trig. CA Geometry: Circle Area Chords Tangent. CA Geometry: Secants and Translations.
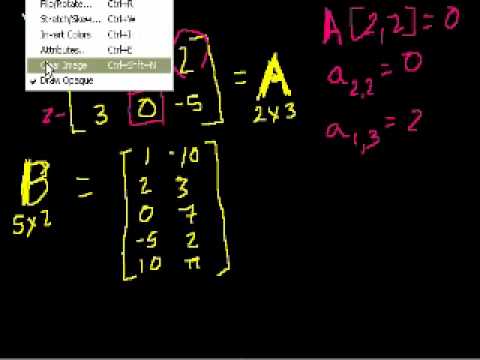
Matrices, vectors, vector spaces, transformations. Covers all topics in a first year college linear algebra course. This is an advanced course normally taken by science or engineering majors after taking at least two semesters of calculus (although calculus really isn't a prereq) so don't confuse this with regular high school algebra. Introduction to matrices. Matrix multiplication (part 1). Matrix multiplication (part 2). Idea Behind Inverting a 2x2 Matrix. Inverting matrices (part 2). Inverting Matrices (part 3). Matrices to solve a system of equations. Matrices to solve a vector combination problem. Singular Matrices. 3-variable linear equations (part 1). Solving 3 Equations with 3 Unknowns. Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A). A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Orthogonal Complements. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes.
Topics covered in a first year course in differential equations. Need to understand basic differentiation and integration from Calculus playlist before starting here. What is a differential equation. Separable Differential Equations. Separable differential equations 2. Exact Equations Intuition 1 (proofy). Exact Equations Intuition 2 (proofy). Exact Equations Example 1. Exact Equations Example 2. Exact Equations Example 3. Integrating factors 1. Integrating factors 2. First order homegenous equations. First order homogeneous equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 2. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 3. 2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 4. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 1. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 2. Complex roots of the characteristic equations 3. Repeated roots of the characteristic equation. Repeated roots of the characteristic equations part 2. Undetermined Coefficients 1. Undetermined Coefficients 2. Undetermined Coefficients 3. Undetermined Coefficients 4. Laplace Transform 1. Laplace Transform 2. Laplace Transform 3 (L{sin(at)}). Laplace Transform 4. Laplace Transform 5. Laplace Transform 6. Laplace Transform to solve an equation. Laplace Transform solves an equation 2. More Laplace Transform tools. Using the Laplace Transform to solve a nonhomogeneous eq. Laplace Transform of : L{t}. Laplace Transform of t^n: L{t^n}. Laplace Transform of the Unit Step Function. Inverse Laplace Examples. Laplace/Step Function Differential Equation. Dirac Delta Function. Laplace Transform of the Dirac Delta Function. Introduction to the Convolution. The Convolution and the Laplace Transform. Using the Convolution Theorem to Solve an Initial Value Prob.
Topics covered in a traditional college level introductory microeconomics course. Production Possibilities Frontier. Opportunity Cost. Increasing Opportunity Cost. Allocative Efficiency and Marginal Benefit. Economic Growth through Investment. Comparative Advantage Specialization and Gains from Trade. Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage. Law of Demand. Price of Related Products and Demand. Changes in Income, Population, or Preferences. Normal and Inferior Goods. Inferior Goods Clarification. Law of Supply. Factors Affecting Supply. Market Equilibrium. Changes in Market Equilibrium. Price Elasticity of Demand. More on Elasticity of Demand. Perfect Inelasticity and Perfect Elasticity of Demand. Constant Unit Elasticity. Total Revenue and Elasticity. More on Total Revenue and Elasticity. Cross Elasticity of Demand. Elasticity of Supply. Elasticity and Strange Percent Changes. Demand Curve as Marginal Benefit Curve. Consumer Surplus Introduction. Total Consumer Surplus as Area. Producer Surplus. Rent Control and Deadweight Loss. Minimum Wage and Price Floors. Taxation and Dead Weight Loss. Percentage Tax on Hamburgers. Taxes and Perfectly Inelastic Demand. Taxes and Perfectly Elastic Demand. Marginal Utility. Equalizing Marginal Utility per Dollar Spent. Deriving Demand Curve from Tweaking Marginal Utility per Dollar. Budget Line. Optimal Point on Budget Line. Types of Indifference Curves. Economic Profit vs Accounting Profit. Depreciation and Opportunity Cost of Capital. Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost.. Visualizing Average Costs and Marginal Costs as Slope. Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. Marginal Revenue Below Average Total Cost. Long Term Supply Curve and Economic Profit. Perfect Competition. Monopoly Basics. Review of Revenue and Cost Graphs for a Monopoly. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 1)- Total Revenue.. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 2)- Marginal Revenue. Monopolist Optimizing Price (part 3)- Dead Weight Loss.avi. Optional Calculus Proof to Show that MR has Twice Slope of Demand. Oligopolies and Monopolistic Competition. Monopolistic Competition and Economic Profit. Oligopolies, Duopolies, Collusion, and Cartels. Prisoners' Dilemma and Nash Equilibrium. More on Nash Equilibrium. Why Parties to Cartels Cheat. Game Theory of Cheating Firms. Negative Externalities. Taxes for Factoring in Negative Externalities. Positive Externalities. Tragedy of the Commons. First Degree Price Discrimination. A Firm's Marginal Product Revenue Curve. How Many People to Hire Given the MPR curve. Adding Demand Curves.
Not all things with four sides have to be squares or rectangles! We will now broaden our understanding of quadrilaterals!. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Whether a Special Quadrilateral Can Exist. Rhombus Diagonals. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Whether a Special Quadrilateral Can Exist. Rhombus Diagonals.
Indefinite integral as anti-derivative. Definite integral as area under a curve. Integration by parts. U-substitution. Trig substitution. Antiderivatives and indefinite integrals. Indefinite integrals of x raised to a power. Antiderivative of hairier expression. Basic trig and exponential antiderivatives. Antiderivative of x^-1. Simple Riemann approximation using rectangles. Generalizing a left Riemann sum with equally spaced rectangles. Rectangular and trapezoidal Riemann approximations. Trapezoidal approximation of area under curve. Riemann sums and integrals. Deriving integration by parts formula. Antiderivative of xcosx using integration by parts. Integral of ln x. Integration by parts twice for antiderivative of (x^2)(e^x). Integration by parts of (e^x)(cos x). U-substitution. U-substitution example 2. U-substitution Example 3. U-substitution with ln(x). Doing u-substitution twice (second time with w). U-substitution and back substitution. U-substitution with definite integral. (2^ln x)/x Antiderivative Example. Another u-substitution example. Riemann sums and integrals. Intuition for Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Evaluating simple definite integral. Definite integrals and negative area. Area between curves. Area between curves with multiple boundaries. Challenging definite integration. Introduction to definite integrals. Definite integrals (part II). Definite Integrals (area under a curve) (part III). Definite Integrals (part 4). Definite Integrals (part 5). Definite integral with substitution. Introduction to trig substitution. Another substitution with x=sin (theta). Integrals: Trig Substitution 1. Trig and U substitution together (part 1). Trig and U substitution together (part 2). Trig substitution with tangent. Integrals: Trig Substitution 2. Integrals: Trig Substitution 3 (long problem). Fundamental theorem of calculus. Applying the fundamental theorem of calculus. Swapping the bounds for definite integral. Both bounds being a function of x. Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Connecting the first and second fundamental theorems of calculus. Introduction to improper integrals. Improper integral with two infinite bounds. Divergent improper integral. Antiderivatives and indefinite integrals. Indefinite integrals of x raised to a power. Antiderivative of hairier expression. Basic trig and exponential antiderivatives. Antiderivative of x^-1. Simple Riemann approximation using rectangles. Generalizing a left Riemann sum with equally spaced rectangles. Rectangular and trapezoidal Riemann approximations. Trapezoidal approximation of area under curve. Riemann sums and integrals. Deriving integration by parts formula. Antiderivative of xcosx using integration by parts. Integral of ln x. Integration by parts twice for antiderivative of (x^2)(e^x). Integration by parts of (e^x)(cos x). U-substitution. U-substitution example 2. U-substitution Example 3. U-substitution with ln(x). Doing u-substitution twice (second time with w). U-substitution and back substitution. U-substitution with definite integral. (2^ln x)/x Antiderivative Example. Another u-substitution example. Riemann sums and integrals. Intuition for Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Evaluating simple definite integral. Definite integrals and negative area. Area between curves. Area between curves with multiple boundaries. Challenging definite integration. Introduction to definite integrals. Definite integrals (part II). Definite Integrals (area under a curve) (part III). Definite Integrals (part 4). Definite Integrals (part 5). Definite integral with substitution. Introduction to trig substitution. Another substitution with x=sin (theta). Integrals: Trig Substitution 1. Trig and U substitution together (part 1). Trig and U substitution together (part 2). Trig substitution with tangent. Integrals: Trig Substitution 2. Integrals: Trig Substitution 3 (long problem). Fundamental theorem of calculus. Applying the fundamental theorem of calculus. Swapping the bounds for definite integral. Both bounds being a function of x. Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Connecting the first and second fundamental theorems of calculus. Introduction to improper integrals. Improper integral with two infinite bounds. Divergent improper integral.
If you can take one figure and flip, shift and rotate (not resize) it to be identical to another figure, then the two figures are congruent. This topic explores this foundational idea in geometry. Congruent Triangles and SSS. SSS to Show a Radius is Perpendicular to a Chord that it Bisects. Other Triangle Congruence Postulates. Two column proof showing segments are perpendicular. Finding Congruent Triangles. Congruency postulates. More on why SSA is not a postulate. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Congruent Triangle Proof Example. Congruent Triangle Example 2. Congruent triangles 1. Congruent triangles 2. Congruent legs and base angles of Isosceles Triangles. Equilateral Triangle Sides and Angles Congruent. Equilateral and Isosceles Example Problems. Triangle types. Triangle angles 1. Another Isosceles Example Problem. Example involving an isosceles triangle and parallel lines. Figuring out all the angles for congruent triangles example. Basic Triangle Proofs Module Example. Basic Triangle Proofs Module Example 2. Basic triangle proofs. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs example 1. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs example 2. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs. Wrong statements in triangle proofs example 1. Wrong statements in triangle proofs. Problem involving angle derived from square and circle. Congruent Triangles and SSS. SSS to Show a Radius is Perpendicular to a Chord that it Bisects. Other Triangle Congruence Postulates. Two column proof showing segments are perpendicular. Finding Congruent Triangles. Congruency postulates. More on why SSA is not a postulate. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Congruent Triangle Proof Example. Congruent Triangle Example 2. Congruent triangles 1. Congruent triangles 2. Congruent legs and base angles of Isosceles Triangles. Equilateral Triangle Sides and Angles Congruent. Equilateral and Isosceles Example Problems. Triangle types. Triangle angles 1. Another Isosceles Example Problem. Example involving an isosceles triangle and parallel lines. Figuring out all the angles for congruent triangles example. Basic Triangle Proofs Module Example. Basic Triangle Proofs Module Example 2. Basic triangle proofs. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs example 1. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs example 2. Fill-in-the-blank triangle proofs. Wrong statements in triangle proofs example 1. Wrong statements in triangle proofs. Problem involving angle derived from square and circle.
Basic probability. Should have a reasonable grounding in basic algebra before watching. Basic Probability. Example: Marbles from a bag. Example: Picking a non-blue marble. Example: Picking a yellow marble. Term Life Insurance and Death Probability. Probability with Playing Cards and Venn Diagrams. Addition Rule for Probability. Compound Probability of Independent Events. Getting At Least One Heads. Example: Probability of rolling doubles. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of making 10 free throws in a row?. LeBron Asks: What are the chances of three free throws versus one three pointer?. Frequency Probability and Unfair Coins. Example: Getting two questions right on an exam. Example: Rolling even three times. Introduction to dependent probability. Example: Dependent probability. Example: Is an event independent or dependent?. Example: Bag of unfair coins. Monty Hall Problem. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Permutations. Combinations. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Conditional Probability and Combinations. Birthday Probability Problem. Random Variables. Discrete and continuous random variables. Probability Density Functions. Expected Value: E(X). Binomial Distribution 1. Binomial Distribution 2. Binomial Distribution 3. Binomial Distribution 4. Expected Value of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Process 1. Poisson Process 2. Law of Large Numbers. Introduction to Random Variables. Probability (part 1). Probability (part 2). Probability (part 3). Probability (part 4). Probability (part 5). Probability (part 6). Probability (part 7). Probability (part 8).
Logarithms. Ex: Converting an exponential to logarithmic statement. Evaluating logarithms. Fancier logarithm expressions. Evaluating logarithms 2. Graphing Logarithmic Functions. Introduction to Logarithms. Introduction to logarithm properties. Introduction to logarithm properties (part 2). Logarithm of a Power. Sum of Logarithms with Same Base. Using Multiple Logarithm Properties to Simplify. Operations with logarithms. Change of Base Formula. Proof: log a + log b = log ab. Proof: A(log B) = log (B^A), log A - log B = log (A/B). Change of base formula proof. Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Logarithmic Scale. Richter Scale. Natural Logarithm with a Calculator. Calculator for Natural Logarithms. Graphing Natural Logarithm Function. Logarithms. Ex: Converting an exponential to logarithmic statement. Evaluating logarithms. Fancier logarithm expressions. Evaluating logarithms 2. Graphing Logarithmic Functions. Introduction to Logarithms. Introduction to logarithm properties. Introduction to logarithm properties (part 2). Logarithm of a Power. Sum of Logarithms with Same Base. Using Multiple Logarithm Properties to Simplify. Operations with logarithms. Change of Base Formula. Proof: log a + log b = log ab. Proof: A(log B) = log (B^A), log A - log B = log (A/B). Change of base formula proof. Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Solving Logarithmic Equations. Logarithmic Scale. Richter Scale. Natural Logarithm with a Calculator. Calculator for Natural Logarithms. Graphing Natural Logarithm Function.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.