Courses tagged with "Calculus I" (77)
Watch fun, educational videos on all sorts of Physics questions. Bridge Design and Destruction! (part 1). Bridge Design (and Destruction!) Part 2. Shifts in Equilibrium. The Marangoni Effect: How to make a soap propelled boat!. The Invention of the Battery. The Forces on an Airplane. Bouncing Droplets: Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces. A Crash Course on Indoor Flying Robots.
This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the second of a six-quarter sequence of classes exploring the essential theor
Nanotechnology is an emerging area that engages almost every technical discipline – from chemistry to computer science – in the study and application of extremely tiny materials. This short course allows any technically savvy person to go one layer beyond the surface of this broad topic to see the real substance behind the very small.
Week 1: A first simple neuron model
Week 2: Hodgkin-Huxley models and biophysical modeling
Week 3: Two-dimensional models and phase plane analysis
Week 4: Two-dimensional models (cont.)/ Dendrites
Week 5: Variability of spike trains and the neural code
Week 6: Noise models, noisy neurons and coding
Week 7: Estimating neuron models for coding and decoding
Before your course starts, try the new edX Demo where you can explore the fun, interactive learning environment and virtual labs. Learn more.
Learn about a new generation of solar cells, organic solar cells, that promise an answer to the energy demands of the future.
The Origins course tracks the origin of all things – from the Big Bang to the origin of the Solar System and the Earth. The course follows the evolution of life on our planet through deep geological time to present life forms.
Physics 101 is the first course in the Introduction to Physics sequence. In general, the quest of physics is to develop descriptions of the natural world that correspond closely to actual observations. Given this definition, the story behind everything in the universe, from rocks falling to stars shining, is one of physics. In principle, the events of the natural world represent no more than the interactions of the elementary particles that comprise the material universe. In practice, however, it turns out to be more complicated than that. As the system under study becomes more and more complex, it becomes less and less clear how the basic laws of physics account for the observations. Other branches of science, such as chemistry or biology, are needed. In principle, biology is based on the laws of chemistry, and chemistry is based on the laws of physics, but our ability to understand something as complex as life in terms of the laws of physics is well beyond our present knowledge. Physics is, however, the…
The physics of the universe appears to be dominated by the effects of four fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear forces, and strong nuclear forces. These forces control how matter, energy, space, and time interact to produce our physical world. All other forces, such as the force you exert in standing up, are ultimately derived from these fundamental forces. We have direct daily experience with two of these forces: gravity and electromagnetism. Consider, for example, the everyday sight of a person sitting on a chair. The force holding the person on the chair is gravitational, and that gravitational force balances with material forces that “push up” to keep the individual in place. These forces are the direct result of electromagnetic forces on the nanoscale. On a larger stage, gravity holds the celestial bodies in their orbits, while we see the universe by the electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) with which it is filled. The electromagnetic force also makes…
Watch fun, educational videos on all sorts of Physics questions. Thomas Young's Double Slit Experiment. Newton's Prism Experiment. Bridge Design and Destruction! (part 1). Bridge Design (and Destruction!) Part 2. Shifts in Equilibrium. The Marangoni Effect: How to make a soap propelled boat!. The Invention of the Battery. The Forces on an Airplane. Bouncing Droplets: Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces. A Crash Course on Indoor Flying Robots. Heat Transfer. Thomas Young's Double Slit Experiment. Newton's Prism Experiment. Bridge Design and Destruction! (part 1). Bridge Design (and Destruction!) Part 2. Shifts in Equilibrium. The Marangoni Effect: How to make a soap propelled boat!. The Invention of the Battery. The Forces on an Airplane. Bouncing Droplets: Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces. A Crash Course on Indoor Flying Robots. Heat Transfer.
This is a 12 week course, currently scheduled to start on Monday, April 14, 2014 and finishing on Friday, July 11. This introductory physics course is intended for physical science majors and others desiring a rigorous introduction to physics. It closely parallels the brick-and-mortar course given to the freshmen at the University of Colorado at Boulder. The course covers classical mechanics, including kinematics, dynamics, conservation laws, and applications.
Physics 140 offers introduction to mechanics, the physics of motion. Topics include: linear motion, vectors, projectiles, relative velocity and acceleration, Newton's laws, particle dynamics, work and energy, linear momentum, torque, angular momentum, gravitation, planetary motion, fluid statics and dynamics, simple harmonic motion, waves and sound. Course Level: Undergraduate This Work, Physics 140 - General Physics 1, by Gus Evrard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license.
This course provides a thorough introduction to the principles and methods of physics for students who have good prepara
This class is an introduction to classical mechanics for students who are comfortable with calculus. The main topics are: Vectors, Kinematics, Forces, Motion, Momentum, Energy, Angular Motion, Angular Momentum, Gravity, Planetary Motion, Moving Frames, and the Motion of Rigid Bodies.
This freshman-level course is the second semester of introductory physics. The focus is on electricity and magnetism. The subject is taught using the TEAL (Technology Enabled Active Learning) format which utilizes small group interaction and current technology. The TEAL/Studio Project at MIT is a new approach to physics education designed to help students develop much better intuition about, and conceptual models of, physical phenomena.
Staff List
Visualizations:
Prof. John Belcher
Instructors:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Bruce Knuteson
Prof. Gunther Roland
Prof. Bolek Wyslouch
Dr. Brian Wecht
Prof. Eric Katsavounidis
Prof. Robert Simcoe
Prof. Joseph Formaggio
Course Co-Administrators:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Robert Redwine
Technical Instructors:
Andy Neely
Matthew Strafuss
Course Material:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Eric Hudson
Dr. Sen-Ben Liao
Acknowledgements
The TEAL project is supported by The Alex and Brit d'Arbeloff Fund for Excellence in MIT Education, MIT iCampus, the Davis Educational Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the Class of 1960 Endowment for Innovation in Education, the Class of 1951 Fund for Excellence in Education, the Class of 1955 Fund for Excellence in Teaching, and the Helena Foundation. Many people have contributed to the development of the course materials. (PDF)
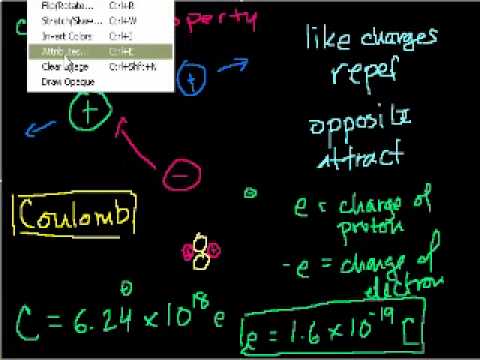
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation. Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law. Electrostatics (part 2). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1). Proof (Advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2). Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential Energy (part 2-- involves calculus). Voltage. Capacitance. Circuits (part 1). Circuits (part 2). Circuits (part 3). Circuits (part 4). Cross product 1. Cross Product 2. Cross Product and Torque. Introduction to Magnetism. Magnetism 2. Magnetism 3. Magnetism 4. Magnetism 5. Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current. Magnetism 7. Magnetism 8. Magnetism 9: Electric Motors. Magnetism 10: Electric Motors. Magnetism 11: Electric Motors. Magnetism 12: Induced Current in a Wire. The dot product. Dot vs. Cross Product. Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation.
Fluids (part 1). Fluids (part 2). Fluids (part 3). Fluids (part 4). Fluids (part 5). Fluids (part 6). Fluids (part 7). Fluids (part 8). Fluids (part 9). Fluids (part 10). Fluids (part 11). Fluids (part 12). Fluids (part 1). Fluids (part 2). Fluids (part 3). Fluids (part 4). Fluids (part 5). Fluids (part 6). Fluids (part 7). Fluids (part 8). Fluids (part 9). Fluids (part 10). Fluids (part 11). Fluids (part 12).
Classical gravity. How masses attract each other (according to Newton). Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2). Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2).
Linear momentum. Conservation of momentum. Elastic collisions. Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2). Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2).
Relationship between angular velocity and speed. Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line. Introduction to Vectors and Scalars. Calculating Average Velocity or Speed. Solving for Time. Displacement from Time and Velocity Example. Acceleration. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Airbus A380 Take-off Time. Airbus A380 Take-off Distance. Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration. Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity. Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity. Projectile Height Given Time. Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time. Impact Velocity From Given Height. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2). Introduction to work and energy. Work and Energy (part 2). Conservation of Energy. Work/Energy problem with Friction. Introduction to mechanical advantage. Mechanical Advantage (part 2). Mechanical Advantage (part 3). Center of Mass. Introduction to Torque. Moments. Moments (part 2). Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Projectile motion (part 1). Projectile motion (part 2). Projectile motion (part 3). Projectile motion (part 4). Projectile motion (part 5). Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Conservation of angular momentum. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2). Viewing g as the value of Earth's Gravitational Field Near the Surface. Intro to springs and Hooke's Law. Potential energy stored in a spring. Spring potential energy example (mistake in math). Introduction to Harmonic Motion. Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus). Harmonic Motion Part 3 (no calculus).
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.