Courses tagged with "Calculus I" (77)
Introduction to Waves. Amplitude, Period, Frequency and Wavelength of Periodic Waves. Introduction to the Doppler Effect. Doppler effect formula when source is moving away. When the source and the wave move at the same velocity. Mach Numbers. Specular and Diffuse Reflection. Specular and Diffuse Reflection 2. Refraction and Snell's Law. Refraction in Water. Snell's Law Example 1. Snell's Law Example 2. Total Internal Reflection. Virtual Image. Parabolic Mirrors and Real Images. Parabolic Mirrors 2. Convex Parabolic Mirrors. Convex Lenses. Convex Lens Examples. Doppler effect formula for observed frequency. Concave Lenses. Object Image and Focal Distance Relationship (Proof of Formula). Object Image Height and Distance Relationship. Introduction to Waves. Amplitude, Period, Frequency and Wavelength of Periodic Waves. Introduction to the Doppler Effect. Doppler effect formula when source is moving away. When the source and the wave move at the same velocity. Mach Numbers. Specular and Diffuse Reflection. Specular and Diffuse Reflection 2. Refraction and Snell's Law. Refraction in Water. Snell's Law Example 1. Snell's Law Example 2. Total Internal Reflection. Virtual Image. Parabolic Mirrors and Real Images. Parabolic Mirrors 2. Convex Parabolic Mirrors. Convex Lenses. Convex Lens Examples. Doppler effect formula for observed frequency. Concave Lenses. Object Image and Focal Distance Relationship (Proof of Formula). Object Image Height and Distance Relationship.
This freshman-level course is the second semester of introductory physics. The focus is on electricity and magnetism. The subject is taught using the TEAL (Technology Enabled Active Learning) format which utilizes small group interaction and current technology. The TEAL/Studio Project at MIT is a new approach to physics education designed to help students develop much better intuition about, and conceptual models of, physical phenomena.
Staff List
Visualizations:
Prof. John Belcher
Instructors:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Bruce Knuteson
Prof. Gunther Roland
Prof. Bolek Wyslouch
Dr. Brian Wecht
Prof. Eric Katsavounidis
Prof. Robert Simcoe
Prof. Joseph Formaggio
Course Co-Administrators:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Robert Redwine
Technical Instructors:
Andy Neely
Matthew Strafuss
Course Material:
Dr. Peter Dourmashkin
Prof. Eric Hudson
Dr. Sen-Ben Liao
Acknowledgements
The TEAL project is supported by The Alex and Brit d'Arbeloff Fund for Excellence in MIT Education, MIT iCampus, the Davis Educational Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the Class of 1960 Endowment for Innovation in Education, the Class of 1951 Fund for Excellence in Education, the Class of 1955 Fund for Excellence in Teaching, and the Helena Foundation. Many people have contributed to the development of the course materials. (PDF)
This class is an introduction to classical mechanics for students who are comfortable with calculus. The main topics are: Vectors, Kinematics, Forces, Motion, Momentum, Energy, Angular Motion, Angular Momentum, Gravity, Planetary Motion, Moving Frames, and the Motion of Rigid Bodies.
This course covers Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics, systems with constraints, rigid body dynamics, vibrations, central forces, Hamilton-Jacobi theory, action-angle variables, perturbation theory, and continuous systems. It provides an introduction to ideal and viscous fluid mechanics, including turbulence, as well as an introduction to nonlinear dynamics, including chaos.
Electromagnetic Theory covers the basic principles of electromagnetism: experimental basis, electrostatics, magnetic fields of steady currents, motional e.m.f. and electromagnetic induction, Maxwell's equations, propagation and radiation of electromagnetic waves, electric and magnetic properties of matter, and conservation laws. This is a graduate level subject which uses appropriate mathematics but whose emphasis is on physical phenomena and principles.
This is the second of a two-semester subject sequence beginning with Atomic and Optical Physics I (8.421) that provides the foundations for contemporary research in selected areas of atomic and optical physics. Topics covered include non-classical states of light–squeezed states; multi-photon processes, Raman scattering; coherence–level crossings, quantum beats, double resonance, superradiance; trapping and cooling-light forces, laser cooling, atom optics, spectroscopy of trapped atoms and ions; atomic interactions–classical collisions, quantum scattering theory, ultracold collisions; and experimental methods.
This is the second course in a two-semester sequence on astrophysics. Topics include galactic dynamics, groups and clusters on galaxies, phenomenological cosmology, Newtonian cosmology, Roberston-Walker models, and galaxy formation.
This course provides an overview of astrophysical cosmology with emphasis on the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation, galaxies and related phenomena at high redshift, and cosmic structure formation. Additional topics include cosmic inflation, nucleosynthesis and baryosynthesis, quasar (QSO) absorption lines, and gamma-ray bursts. Some background in general relativity is assumed.
8.962 is MIT's graduate course in general relativity, which covers the basic principles of Einstein's general theory of relativity, differential geometry, experimental tests of general relativity, black holes, and cosmology.
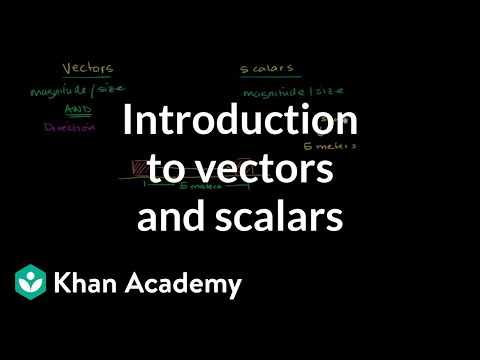
In this tutorial we begin to explore ideas of velocity and acceleration. We do exciting things like throw things off of cliffs (far safer on paper than in real life) and see how high a ball will fly in the air. Introduction to Vectors and Scalars. Calculating Average Velocity or Speed. Solving for Time. Displacement from Time and Velocity Example. Acceleration. Airbus A380 Take-off Time. Airbus A380 Take-off Distance. Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line. Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration. Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff. Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity. Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity. Projectile Height Given Time. Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time. Impact Velocity From Given Height. Viewing g as the value of Earth's Gravitational Field Near the Surface. Projectile motion (part 1). Projectile motion (part 2). Projectile motion (part 3). Projectile motion (part 4). Projectile motion (part 5). Introduction to Vectors and Scalars. Calculating Average Velocity or Speed. Solving for Time. Displacement from Time and Velocity Example. Acceleration. Airbus A380 Take-off Time. Airbus A380 Take-off Distance. Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line. Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration. Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff. Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity. Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity. Projectile Height Given Time. Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time. Impact Velocity From Given Height. Viewing g as the value of Earth's Gravitational Field Near the Surface. Projectile motion (part 1). Projectile motion (part 2). Projectile motion (part 3). Projectile motion (part 4). Projectile motion (part 5).
Linear momentum. Conservation of momentum. Elastic collisions. Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2). Introduction to Momentum. Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball. 2-dimensional momentum problem. 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2).
Thinking about making things rotate. Center of mass, torque, moments and angular velocity. Center of Mass. Introduction to Torque. Moments. Moments (part 2). Relationship between angular velocity and speed. Conservation of angular momentum. Center of Mass. Introduction to Torque. Moments. Moments (part 2). Relationship between angular velocity and speed. Conservation of angular momentum.
You understand velocity and acceleration well in one-dimension. Now we can explore scenarios that are even more fun. With a little bit of trigonometry (you might want to review your basic trig, especially what sin and cos are), we can think about whether a baseball can clear the "green monster" at Fenway Park. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2.
Work and energy. Potential energy. Kinetic energy. Mechanical advantage. Springs and Hooke's law. Introduction to work and energy. Work and Energy (part 2). Conservation of Energy. Work/Energy problem with Friction. Introduction to mechanical advantage. Mechanical Advantage (part 2). Mechanical Advantage (part 3). Intro to springs and Hooke's Law. Potential energy stored in a spring. Spring potential energy example (mistake in math). Introduction to work and energy. Work and Energy (part 2). Conservation of Energy. Work/Energy problem with Friction. Introduction to mechanical advantage. Mechanical Advantage (part 2). Mechanical Advantage (part 3). Intro to springs and Hooke's Law. Potential energy stored in a spring. Spring potential energy example (mistake in math).
Classical gravity. How masses attract each other (according to Newton). Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2). Introduction to Gravity. Mass and Weight Clarification. Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit. Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster. Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station. Space Station Speed in Orbit. Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation. Gravitation (part 2).
Pendulums. Slinkies. You when you have to use the bathroom but it is occupied. These all go back and forth over and over and over again. This tutorial explores this type of motion. Introduction to Harmonic Motion. Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus). Harmonic Motion Part 3 (no calculus). Introduction to Harmonic Motion. Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus). Harmonic Motion Part 3 (no calculus).
Watch fun, educational videos on all sorts of Physics questions. Bridge Design and Destruction! (part 1). Bridge Design (and Destruction!) Part 2. Shifts in Equilibrium. The Marangoni Effect: How to make a soap propelled boat!. The Invention of the Battery. The Forces on an Airplane. Bouncing Droplets: Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces. A Crash Course on Indoor Flying Robots.
The Origins course tracks the origin of all things – from the Big Bang to the origin of the Solar System and the Earth. The course follows the evolution of life on our planet through deep geological time to present life forms.
An introduction to modern astronomy's most important questions. The four sections of the course are Planets and Life in The Universe; The Life of Stars; Galaxies and Their Environments; The History of The Universe.
Physics 101 is the first course in the Introduction to Physics sequence. In general, the quest of physics is to develop descriptions of the natural world that correspond closely to actual observations. Given this definition, the story behind everything in the universe, from rocks falling to stars shining, is one of physics. In principle, the events of the natural world represent no more than the interactions of the elementary particles that comprise the material universe. In practice, however, it turns out to be more complicated than that. As the system under study becomes more and more complex, it becomes less and less clear how the basic laws of physics account for the observations. Other branches of science, such as chemistry or biology, are needed. In principle, biology is based on the laws of chemistry, and chemistry is based on the laws of physics, but our ability to understand something as complex as life in terms of the laws of physics is well beyond our present knowledge. Physics is, however, the…
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.